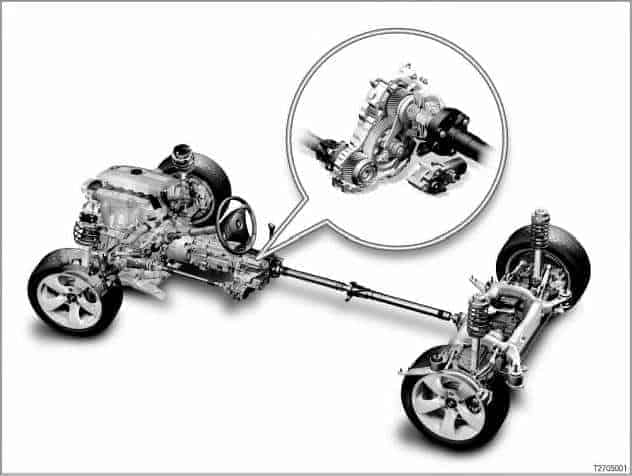
Inleiding:
Voor- of achterwielaandrijving wil zeggen op welke wielen de aandrijfkrachten van de motor over worden gebracht. De meeste autofabrikanten kiezen voor voorwielaandrijving. De motor zorgt voor de aandrijfkrachten. Bij een handgeschakelde versnellingsbak wordt de versnellingsbak met de koppeling bediend, bij een automatische versnellingsbak gebeurt dit in de bak zelf. Via de aandrijfassen komt de kracht uiteindelijk bij de wielen terecht.
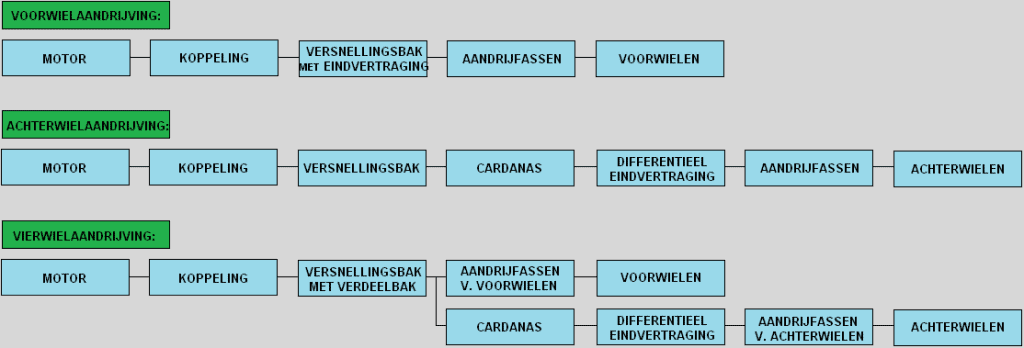
Voorwielaandrijving:
Bij voorwielaandrijving staan de voorwielen met de aandrijfassen gekoppeld aan de versnellingsbak (met inwendig differentieel). Meestal is het motorblok dwars geplaatst om ruimte te besparen. Autofabrikanten kiezen vaak voor voorwielaandrijving. Dit is goedkoper dan achter- of vierwielaandrijving omdat er minder materialen gebruikt worden, en het is meer ruimtebesparend en minder gevoelig voor trillingen dan voorwielaandrijving.
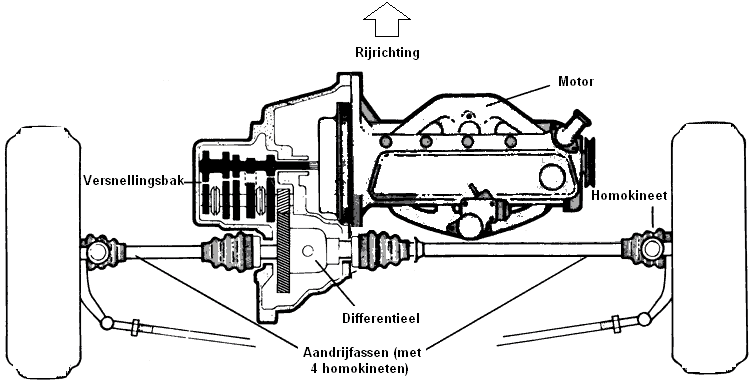
Achterwielaandrijving:
Bij auto’s met achterwielaandrijving ligt het motorblok in de lengte. Vanaf de versnellingsbak loopt er een cardanas (of tussenas) onder de auto door (die boven de uitlaat uit het zicht geplaatst wordt) naar het cardan.
Auto’s met veel vermogen en achterwielaandrijving zijn vaak gevoeliger voor overstuur (de auto maakt dan een grotere bocht dan nodig, de achterkant wil de voorkant voorbij). Een optie als ASR is daarom geen overbodige luxe. Achterwielaandrijving wordt door de fabrikanten minder toegepast als voorwielaandrijving. Vooral auto’s die veel vermogen moeten leveren (waaronder BMW en Mercedes) worden met op de achterwielen aangedreven. Ook willen zij een ideale gewichtsverdeling tussen de voor- en achteras hebben. Door de motor in lengterichting te plaatsen, hangt de versnellingsbak onder het middenconsole in het interieur. De versnellingsbak is dus dichter in de buurt van de achteras geplaatst. Het zwaartepunt wordt nu dus meer naar achteren verplaatst.
Een ander voordeel is dat er op deze manier meer vermogen op het wegdek overgebracht kan worden. Bij het stevig accelereren met een auto met meer dan 250 pk zal het gewicht op de achterwielen van de auto veel groter worden, net als dat bij het remmen het gewicht op de voorwielen toeneemt. Bij het optrekken neemt het gewicht dus toe op de achterwielen, waardoor de kans op doorslippen vele malen minder dan wanneer de auto op de voorwielen aangedreven zou zijn.
Auto’s met achterwielaandrijving hebben ook een speciaal gevormde brandstoftank, omdat de cardanas en het cardan er onder gemonteerd zitten. Er wordt dan een zadeltank met een extra zuigstraal-(brandstof)pomp gemonteerd.
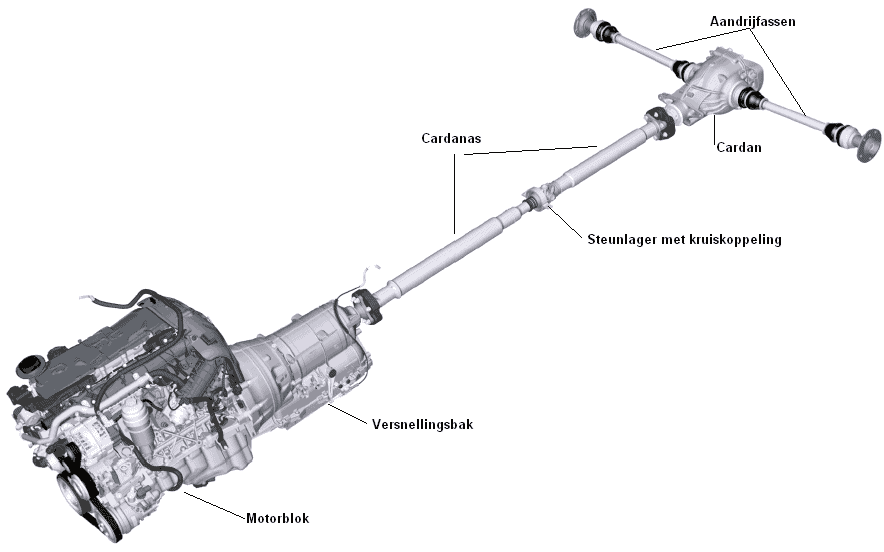
Vierwielaandrijving:
Bij auto’s met vierwielaandrijving, worden zoals de naam het al zegt, alle vier de wielen aangedreven.
Het voordeel hier van is dat al het motorvermogen gebruikt kan worden om te accelereren zonder dat er wielen doorslippen en dat er veel meer grip is op onverharde wegen. Terreinauto’s hebben vaak vierwielaandrijving, omdat er met behulp van het ASR systeem vaak ook voldoende vermogen kan worden overgebracht op ondergronden waar enkel een voorwiel- of achterwielaangedreven auto op vast komt te staan (denk aan sneeuw, zand of modder). Ook sportieve auto’s met veel vermogen worden soms met vierwielaandrijving uitgevoerd.
Er zijn verschillende systemen, waarbij er geen permanente aandrijving op alle vier de wielen tegelijk is. Er worden op deze website twee verschillende systemen beschreven, namelijk van de Haldex-koppeling en van een verdeelbak die aan de versnellingsbak gemonteerd zit.
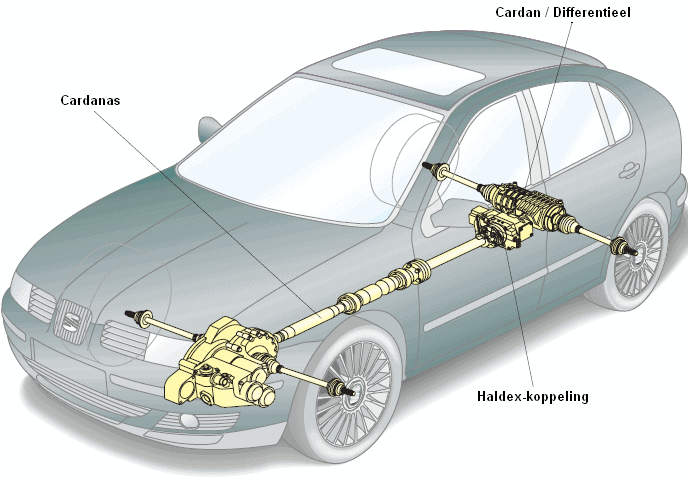
Haldex-koppeling:
Toegepast op VAG merken; VW, Audi, Seat en Skoda. De haldex-koppeling zit geplaatst bij de achtera, en regelt de aandrijfkrachten van de cardanas op de aandrijfassen van de wielen. De voorwielen zijn constant aangedreven.
Klik hier voor meer informatie over de Haldex-koppeling.
Verdeelbak:
Toegepast bij o.a. BMW. De verdeelbak zit aan de versnellingsbak gemonteerd en regelt de aandrijfkrachten naar de voorwielen.
De achterwielen zijn hier bij direct verbonden met de versnellingsbak en worden altijd aangedreven.

