Refrigerant: function and operation
Refrigerants play a crucial role in A/C systems by transporting heat from the evaporator to the condenser. In doing so, the refrigerant undergoes two phase changes: in the evaporator it changes from liquid to gas, and in the condenser from gas to liquid. This process ensures that the absorbed heat is effectively released to the outside air.
In the automotive industry, different types of refrigerants are used, each with specific properties that determine the choice. Important factors include:
- Boiling point: Important for the phase change in the system.
- Cost: Influences economic feasibility.
- Environmental effects: Impact on the environment, such as ozone depletion and the greenhouse effect.
- Regulations: Laws and regulations that restrict or prohibit the use of certain refrigerants.
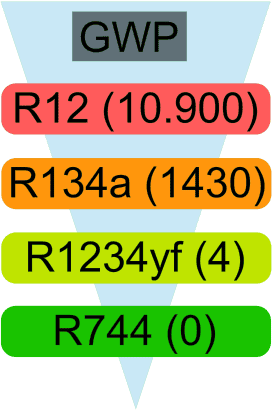
GWP (Global Warming Potential):
GWP (Global Warming Potential) is determined by scientific organizations such as the IPCC, which use advanced climate models to calculate the influence of gases on global warming. GWP measures the warming potential of different gases compared to carbon dioxide (CO₂), for which the GWP is set to 1. This helps in making environmentally friendly choices and limiting emissions of gases with a high GWP.
GWP indicates how much more warming a gas causes compared to CO₂ over a period of 100 years. For example, the GWP of R12 is 10,900, which means that one kilogram of R12 has the same warming effects as 10,900 kilograms of CO₂. This corresponds to the emissions of a gasoline car driving 68,000 km with a fuel economy of 1 in 15. The GWP of R744 is 1, because this refrigerant is CO₂ and is therefore compared to itself.
In the next paragraph, the most commonly used refrigerants in vehicles are described, where GWP has played an important role in the switch to newer refrigerants.
Commonly used refrigerants in motor vehicles:
In the automotive sector, we currently find R134a, R1234yf, and the newer R744 refrigerant. We only encounter R12 at most in classic vehicles.
- R12 was widely used in vehicle air conditioning systems in the past. It is a refrigerant made up of carbon atoms (C), chlorine atoms (Cl), and fluorine atoms (F), with the chemical formula CCl₂F₂. R12 belongs to the group of CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons), also referred to as CFC12. Due to its harmful effect on the ozone layer (GWP of 10,900), R12 has been banned since January 1, 1995.
- R134a was introduced in 1992 as a replacement for R12. This refrigerant contains HFCs (hydrofluorocarbons) and is less harmful to the environment. R134a contains no chlorine, making it a more environmentally friendly alternative. The formula of R134a is C₂H₂F₄, and it is also referred to as HFC134a or tetrafluoroethane. The lowercase letter ‘a’ in the name indicates variations in chemical structures with the same atomic composition. Although R134a does not damage the ozone layer, it has a higher GWP (Global Warming Potential) value of 1430. This means it has a significant greenhouse effect, although it is less harmful than R12.
- R1234yf is a hydrofluoro-olefin (HFO) and has replaced R134a since January 1, 2011. It has a much lower GWP value of 4, which means the greenhouse effect of R1234yf is about 300 times lower than that of R134a. Despite this lower GWP value, the greenhouse effect of R1234yf is still about four times higher than that of CO₂ (R744). R1234yf is mildly flammable and its chemical formula is C₃H₂F₄. It complies with F-gases regulations, but the fire risk is slightly higher compared to other refrigerants.
- R744 (CO₂), better known as carbon dioxide (CO₂), is an environmentally friendly refrigerant with a GWP value of only 1, making it an attractive alternative to other refrigerants such as R134a and R1234yf. The molecular structure of R744 is much smaller than that of R1234yf. This refrigerant operates at high pressures up to 140 bar, which requires special system designs, because conventional systems are usually not suitable for such pressure levels. R744 has excellent thermodynamic properties, allowing it to efficiently move large amounts of heat with a small volume. This results in compact and efficient systems. It is increasingly used in commercial and industrial refrigeration systems, as well as in vehicle air conditioning, and also in electric vehicles with a heat pump.

Molecular composition:
Internationally, refrigerants are designated with an “R”, which stands for “Refrigerant”. The numbers after the “R” indicate the molecular composition of the refrigerant. The meaning of the numbers is as follows:
- The first digit after the “R” indicates the number of carbon atoms minus one. If there is no first digit, the number of carbon atoms is 1.
- The second digit indicates the number of hydrogen atoms plus one.
- The third digit indicates the number of fluorine atoms.
Chlorine atoms are not listed in the R code. Below, the molecular compositions of the four refrigerants that we encounter in automotive engineering are shown.
R12:
The chemical formula for R12 is CCl₂F₂, which means the molecule consists of one carbon atom, no hydrogen atoms, two fluorine atoms, and two chlorine atoms. The chlorine atoms are not listed in the R code, but they are part of the molecular structure.
- First digit (1): Indicates the number of carbon atoms minus one (C₁ – 1 = 0). If there is no first digit, this means the number of carbon atoms is 1.
- Second digit (1): Number of hydrogen atoms minus one (H₀ – 1 = -1, so 0 hydrogen atoms)
- Third digit (2): Number of fluorine atoms (F₂)
R134a:
Chemical formula: C₂H₂F₄, which means the molecule consists of two carbon atoms, two hydrogen atoms, and four fluorine atoms. This refrigerant contains no chlorine atoms.
- First digit (1): Number of carbon atoms minus one (C₂ – 1 = 1)
- Second digit (3): Number of hydrogen atoms plus one (H₂ + 1 = 3)
- Third digit (4): Number of fluorine atoms (F₄)
- a: Indicates the specific isomer of tetrafluoroethane, namely 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane
R1234yf:
The chemical formula for R1234yf is C₃H₂F₄, which means the molecule consists of three carbon atoms, two hydrogen atoms, and four fluorine atoms. This refrigerant contains no chlorine atoms.
- First digit (1): Indicates that the molecule contains a double bond
- Second digit (2): Number of carbon atoms minus one (C₃ – 1 = 2)
- Third digit (3): Number of hydrogen atoms plus one (H₂ + 1 = 3)
- Fourth digit (4): Number of fluorine atoms (F₄)
- y: Indicates the position of the double bond and the specific structure of the molecule
- f: Identifies the specific isomer of tetrafluoropropene, namely 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene
R744 (CO₂):
R744 is a special designation for carbon dioxide (CO₂). The chemical formula for R744 is CO₂, which means the molecule consists of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. This refrigerant contains no hydrogen atoms or fluorine atoms.
- First digit (7): The “7” indicates that it is an inorganic refrigerant. For inorganic compounds, the numbers are not interpreted in the same way as for organic refrigerants
- Second digit (4): In this specific case, “744” is simply a standardized code and does not have the same meaning as with organic refrigerants. It simply indicates that it is CO₂.
- Third digit (4): See the explanation of the second digit
Service with an A/C service station:
To evacuate and recharge the A/C system, an A/C service station is required. This device also checks whether the system is free of leaks. After evacuating, the refrigerant and the compressor oil are weighed. This provides insight into how much the system has leaked down over the past months or years. A properly functioning system may leak down by a maximum of 10% per year. However, with leaks, this percentage can increase much faster. If the A/C system has never received service (meaning evacuating and recharging the system), after a few years (for example up to 8 years) it can become so low that it no longer functions properly. This can lead to damage to the A/C compressor. With some luck, the system can work again by recharging it. It is therefore recommended to have the system serviced every 2 to 4 years.
An A/C check is not the same as service. Sometimes during a check only the air temperature is measured and a conclusion is drawn about whether the system works properly. Therefore, when having service performed, clearly ask whether the system is being evacuated and recharged.

For more explanation about air conditioning, see the chapter air conditioning.
Related page:
