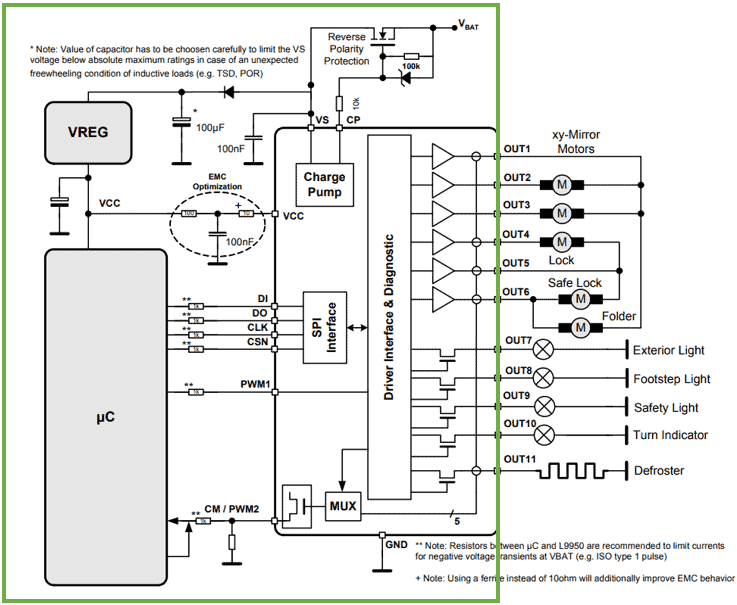
Introduction:
This page explains the purpose of the components in an ECU. Most of the text and images have been compiled by Mr. W. Tulp for his own lessons and are published here with his permission.
A Technical Specialist for passenger cars / commercial vehicles must have the knowledge and skills to make diagnoses. This website contains information on measurement techniques, sensor signal processing, and various cases under the “Diagnostic Techniques” section. The information on this page delves into the functioning of the components inside the ECU, using the engine control unit of Peugeot / Citroën as an example.
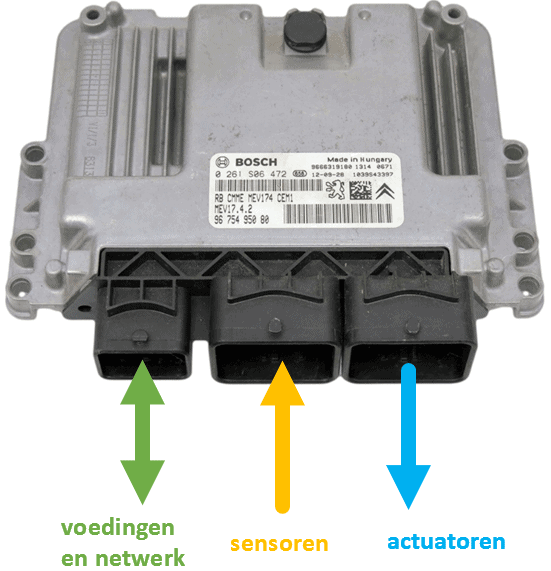
Components in an ECU with explanation:
This page currently provides a brief explanation of the components indicated in the image on the ECU’s circuit board.
A more detailed explanation of the components found in this ECU will be available soon.
SMD284 pressure sensor:
- Surface mount piezoresistive silicon absolute pressure sensor 60 – 115 kPa
- Pressure sensor for the (atmospheric) outside air pressure. The sensor measures air pressure through an opening in the housing (see photo).
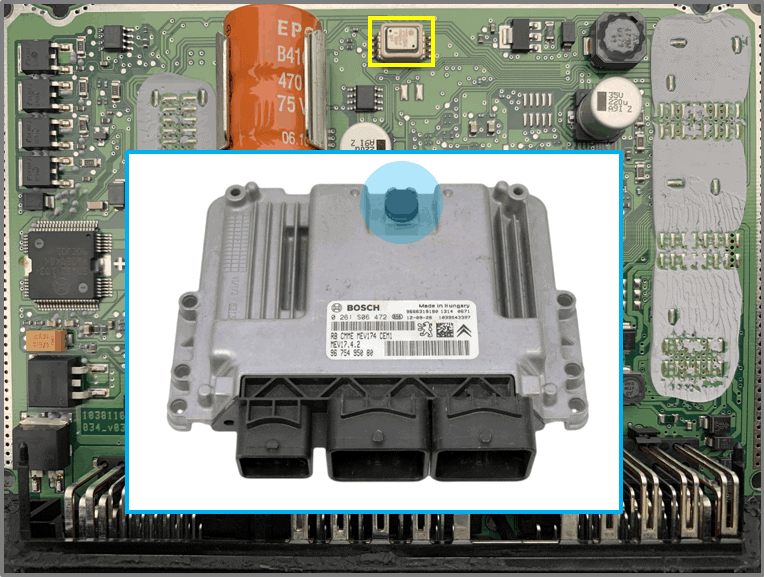
Connector:
- sensors:
– thin connections
– low current strengths - actuators:
– thick connections
– high current strengths - power connections
- networks
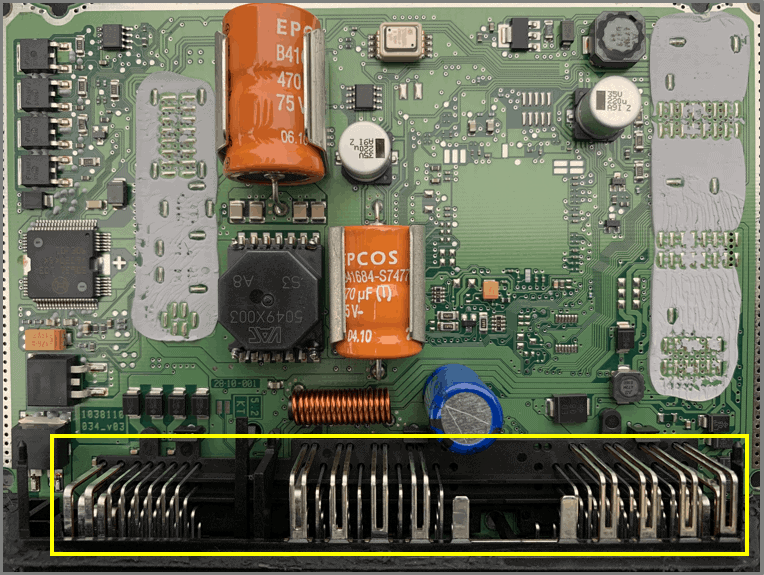
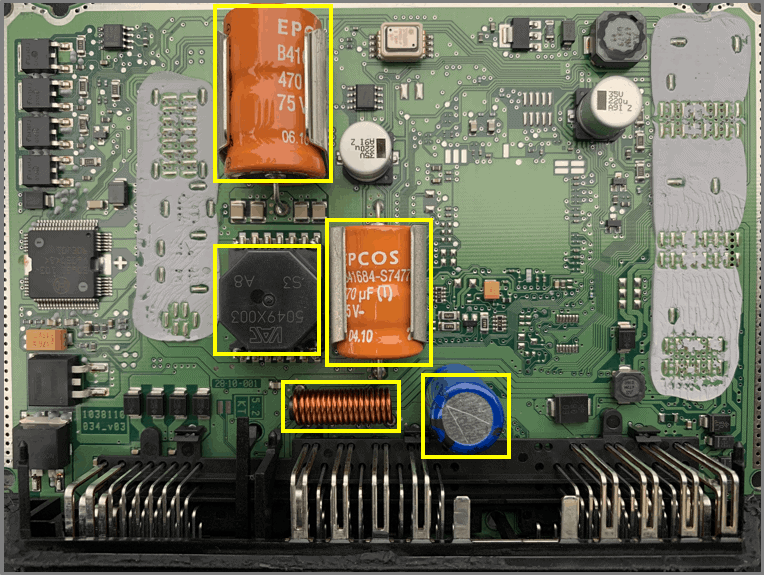
- capacitor 1
– 470 uF
– 75 V
protection in combination with? - capacitor 2
– 470 uF
– 35 V
smoothing capacitor - coil
– EMC filtering
– induction voltages - VAC 5049X003 (thanks to ACtronics)
– switching power supply transformer
– power supply for injectors
- Opamp LM2904
– function unknown
– in the vicinity of other circuitry
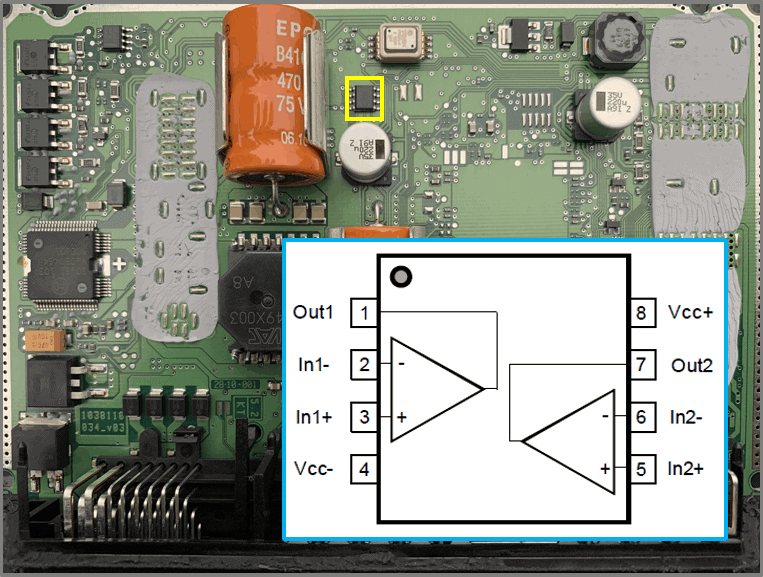
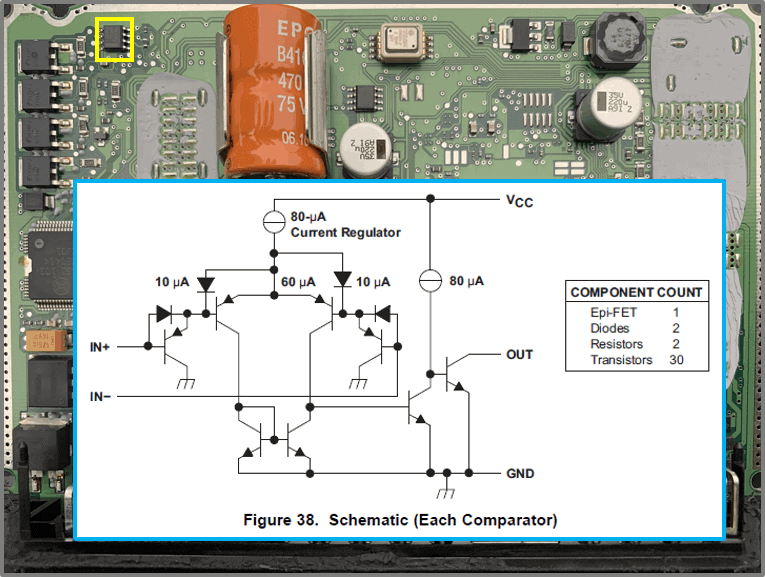
- Opamp LM2903
– comparator
– comparator of two voltages
– internal schema
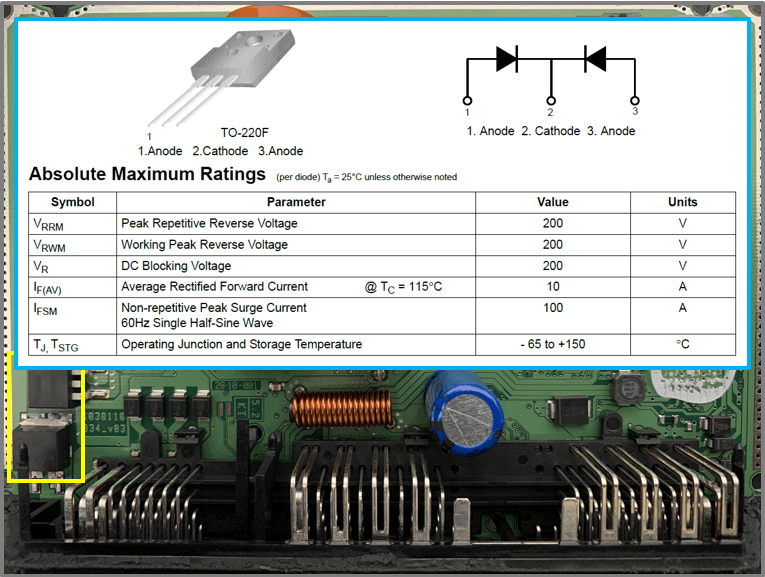
- Rectifier F20UP20DN
– Ultrafast Recovery Power Rectifier
– Ultrafast: <45 ns
– Max. current: 10 A
– go to connectors: C1, D1, E1, F1
- Protection circuit against:
– short circuit
– high temperatures
– high currents (overload)
– over and under voltage
– electrostatic discharge
– reverse battery connection - Applications:
– bcC power switch for grounded 12-volt load
– for all types of resistive, inductive, and capacitive loads
– replaces electromechanical relays and discrete circuits
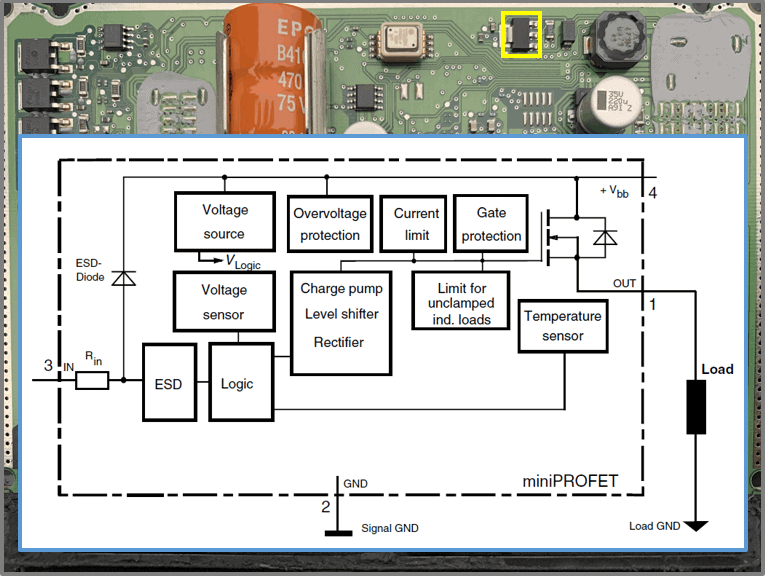
Ignition and injection:
- DA36FJ: four FETs stacked, according to the schematic they go to the coils
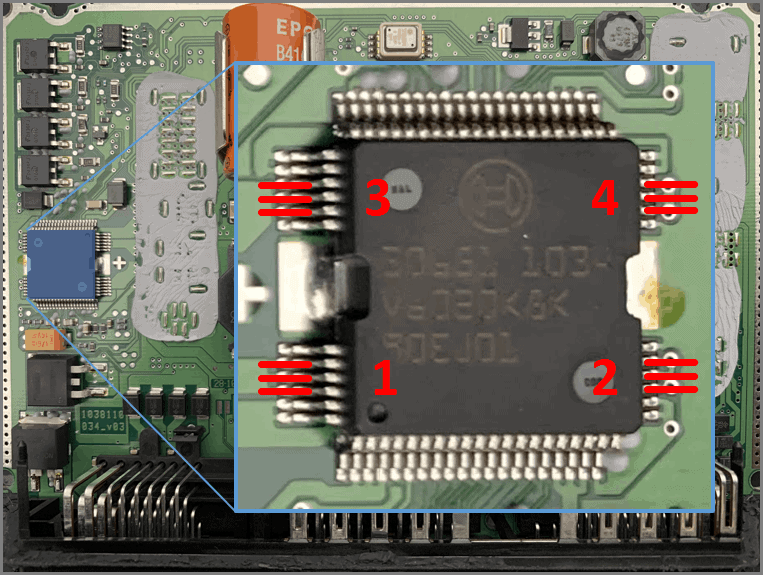
- Beneath these FETs is the IC: 30651 (Car injection drive chip)
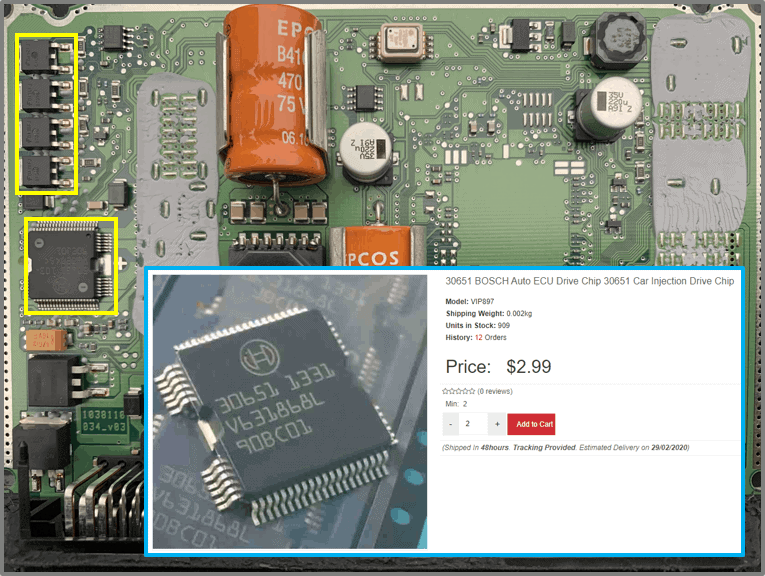
Car Injection Drive Chip:
- Three connections per injector on the IC
Diodes:
- Type ED08
- anode goes to the injectors
- cathode is collectively connected to positive
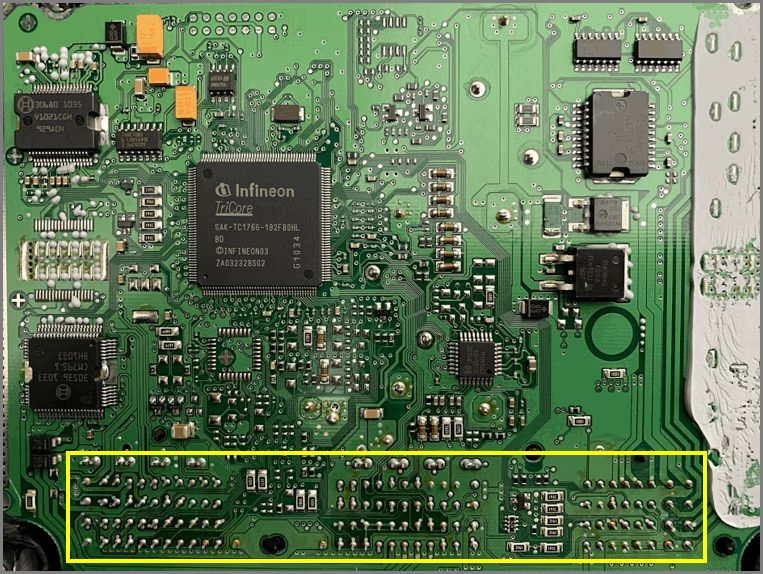
Bottom of ECU. Framed: solder connections of the connector
Custom made IC:
- type 30536
- OEM: Original Equipment Manufacturer (specifically made for manufacturers)
- Integrated final stages
- Control of coils and/or lambda sensor heater control.
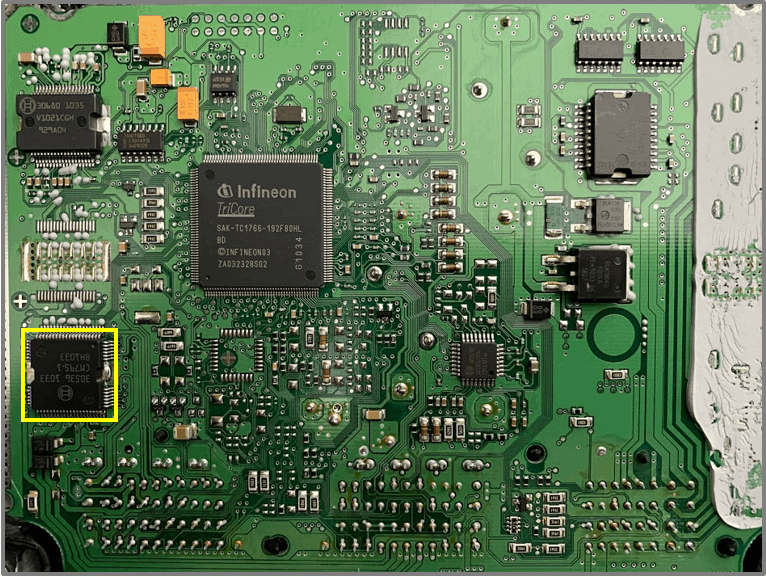
Custom made IC (2):
- type: 30680
- power supply for ECU electronics
- 5.0 and 3.6 volts
- three times protected 5.0 volt sensors
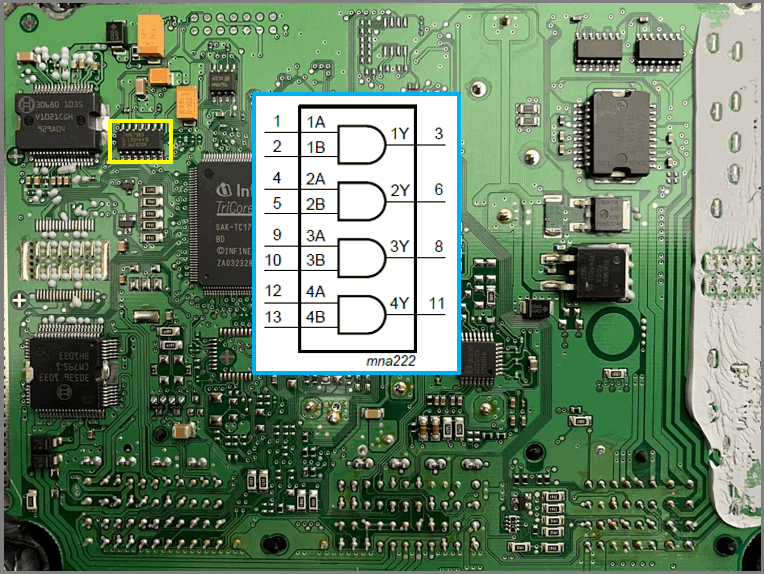
Digital IC
- type: 74HCT08
- AND gates
- IC30680 provided with logical data
Car ECU driver auto CPU programmer accessories
- type: 30530
- in PDF datasheet (page 4 of 117): Dedicated Emulation Device chip for multi-core debugging, tracing and calibration via USB V1.1 interface available (TC1766ED)
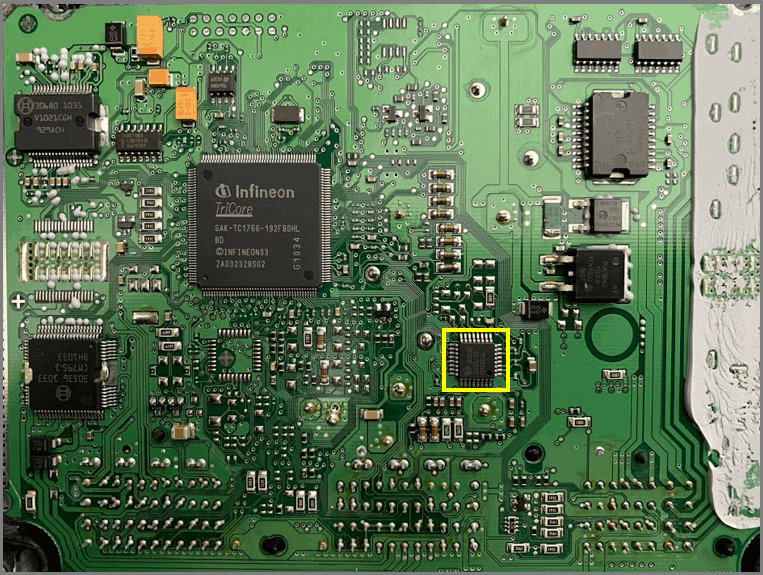
Electric motor control:
- Type: TLE7209
- H-bridge
- M29 DC throttle stepper motor control
- The H-bridge is protected against:
– high temperatures
– short circuit
– overvoltage - For all aforementioned faults, the FETs will open (Tri-state)
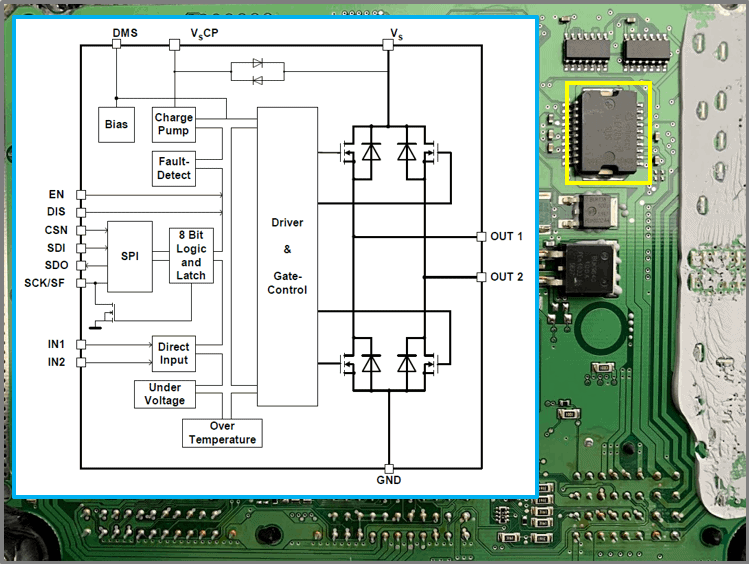
H-bridge control from M29:
- 74HCT00
– digital IC
– NAND gates - 74HCT08
– digital IC
– AND gates
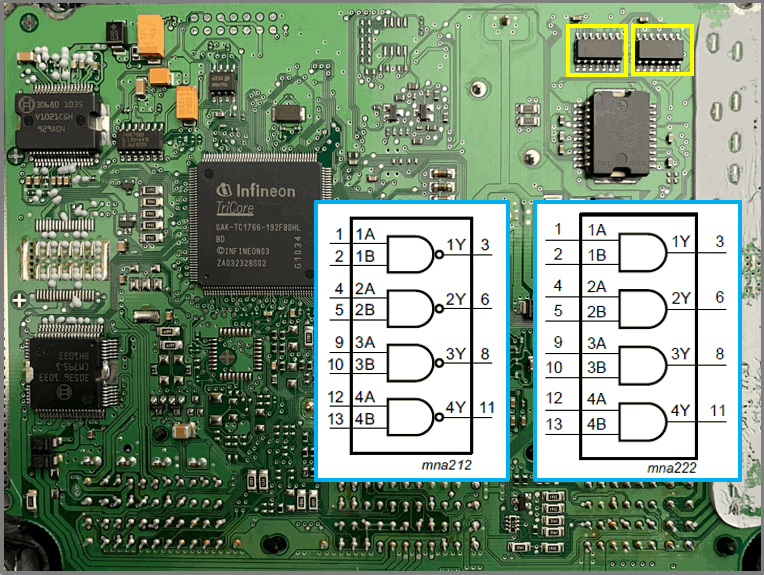
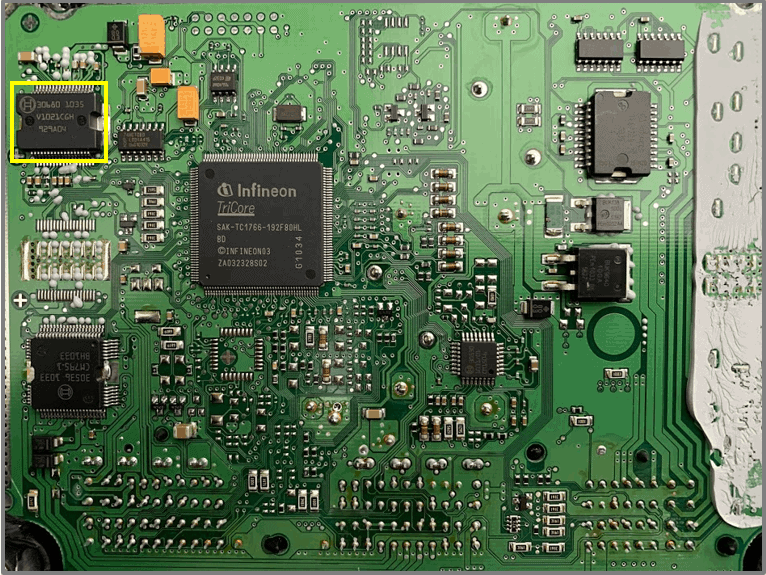
FET – BUK9640
- Function of the FET is unknown
- One side is connected to ground
- Connection to the connector is not found
- Power circuit to ECU is indicated in blue in the image.
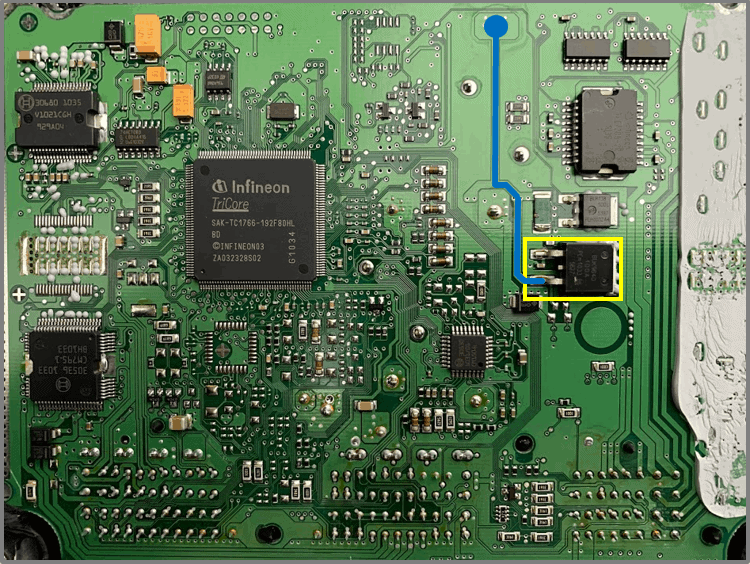
FET – BUK138
- Constant power supply to pin 21 in the large connector.
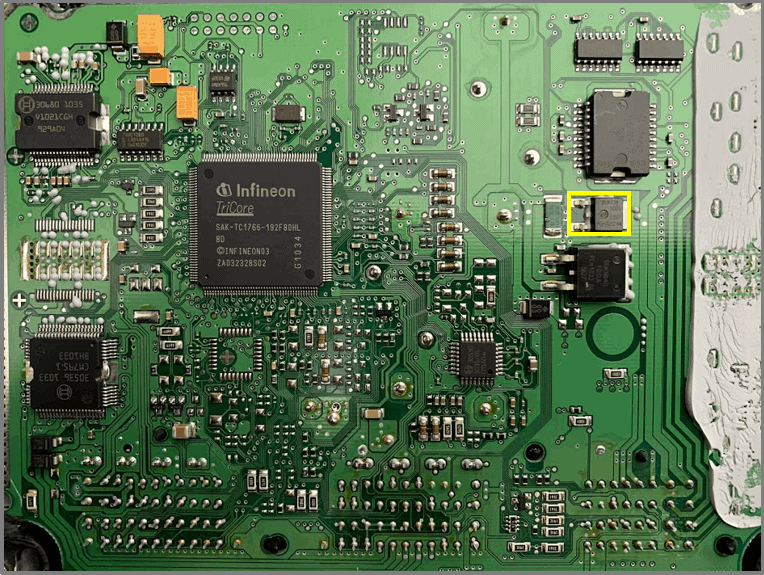
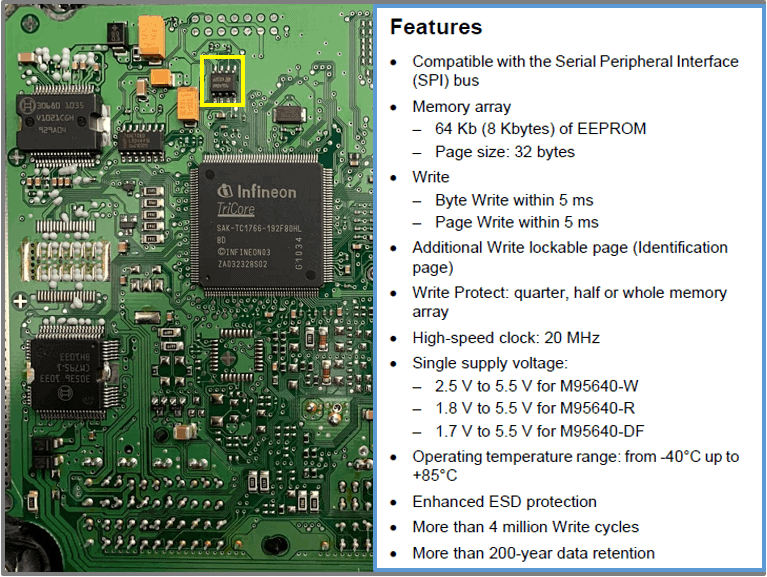
EEPROM
- 64-Kbit serial SPI bus EEPROM with high-speed clock
- Type: 95640W
- SPI: Serial Peripheral Interface (Serial interface (master/slave)
– Advantages: simple hardware, addressing not needed, low power consumption
– Disadvantages: no control by the slave, no error checking
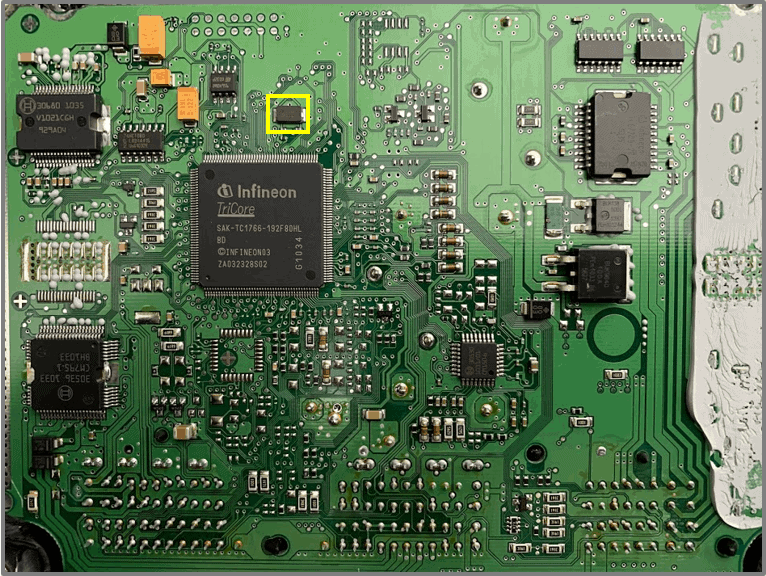
Clock
- Clock 20,000 kHz = 20 MHz for EEPROM
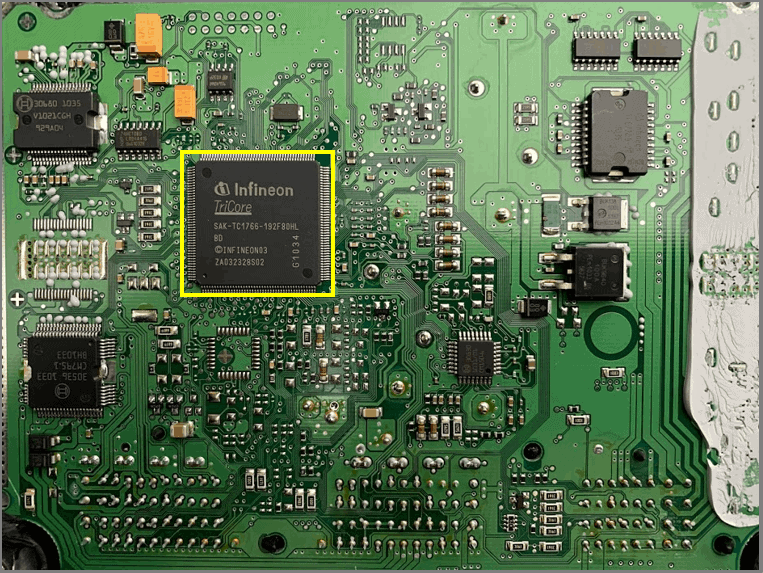
Processor
- All memories are in the processor
- 32-bit Tricore 80 MHz
- 56 Kb local data SRAM (LMB)
- 1504 Kbyte Program Flash
- 16 Kbyte boot ROM
- 64-bit bus to LMD
- 32 analog inputs for ADC
- 81 digital I/O lines
Output
- Signals from ECU to the actuators
– via driver ICs
– transistor. Advantage: large currents possible. Disadvantage: current-driven.
– FET transistor. Advantage: voltage-driven. Disadvantage: low current strengths.
– IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor). Advantages of transistor and FET, thus both large currents possible and voltage-driven.