Topics:
Door Lock:
Door locks are mounted in the doors. These are used to open and close the doors. They also serve a safety purpose, preventing the door from accidentally opening during an accident. The doors must be easily opened by emergency services if an accident occurs.
Door locks can be locked and unlocked mechanically with a key or electronically via a control unit. The electronic operation is often part of the central locking system, which is discussed in the next paragraph.
Door locks can only be disassembled when the interior trim is removed. In older cars, the lock can be unscrewed from the outside, but this is too vulnerable to crime. Therefore, disassembly is made as difficult as possible. Sometimes the entire window mechanism, including the window, must be removed.

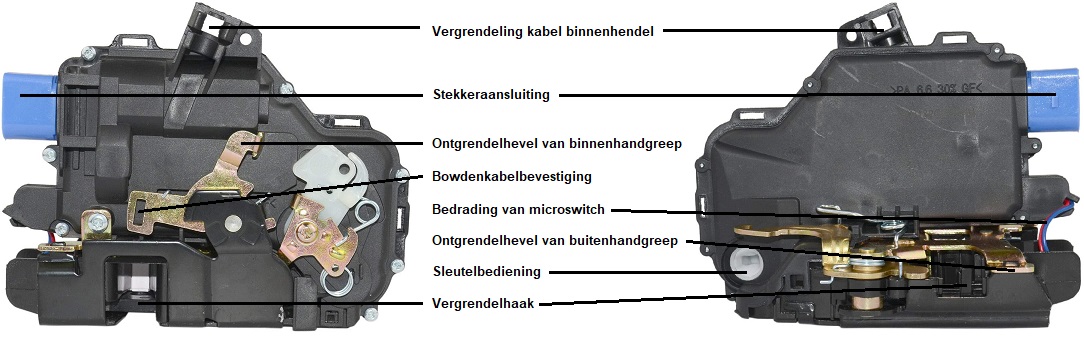
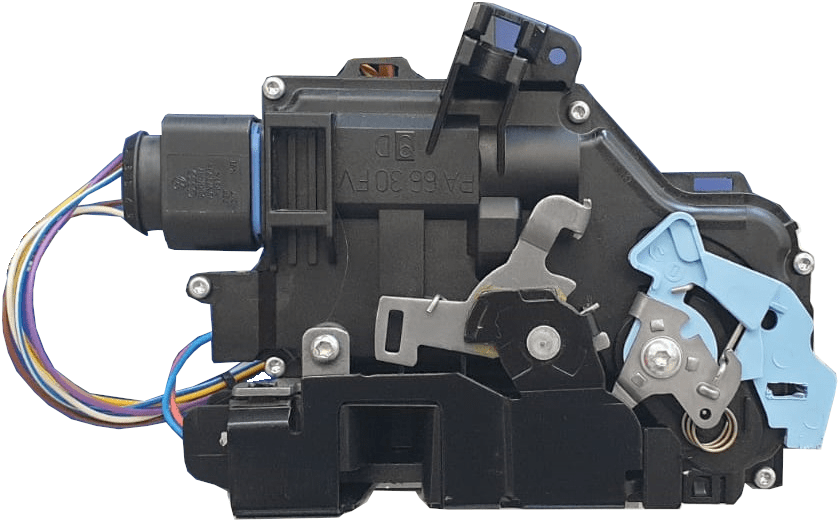
The image below shows a door lock module from two sides. This lock has an integrated electronic control unit that locks and unlocks the lock on command. At the top, we see a locking clip for the Bowden cable of the inner handle. The end of this cable is connected to the Bowden cable attachment. When the inner handle is operated, the unlocking lever tilts to open the locking hook. The unlocking lever of the outer handle is slightly less visible but works in the same way. Additionally, we see the wiring of the internal microswitch which registers the position of the locking hook, so that the interior lighting, indicator lamps, and alarm respond to the opening of the lock. Lastly, we see the key operation; when you insert the key blade into the lock cylinder, the end of the key fits into this slot. When it is possible to turn the key (the lock cylinder rotates), this part will rotate within the lock module to mechanically unlock or lock.
Central Locking:
In recent years, individual door locking has more and more been replaced by central locking. By manually operating the lock cylinder in the driver’s door, the locks of the other doors and the tailgate are also controlled, receiving the command “open” or “close”. Nowadays, almost all cars are equipped with remote control. An extension of this is automatic operation with remote control or comfort access; here, no physical contact is required between the key and the vehicle to operate the central locking.
The central locking ensures that a locking pawl in the door lock is shifted. This can be done in several ways:
- pneumatically;
- electromagnetically;
- via an electric motor.
Pneumatic:
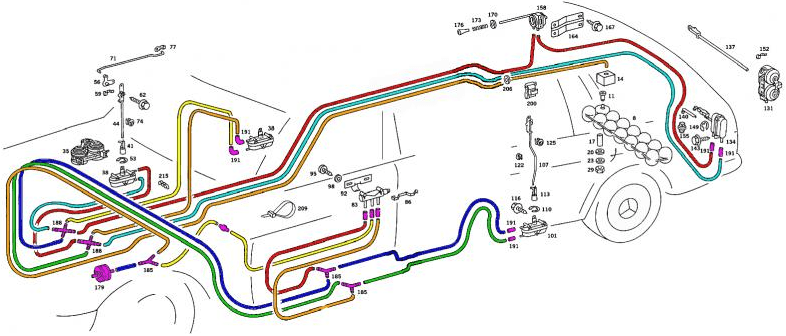
Until the late ’80s and early ’90s, some manufacturers used vacuum-controlled central locking. Using vacuum, the lock actuators were changed position (opened or locked). A diaphragm pump enables alternating positive or negative pressure. Each door lock contains a diaphragm chamber where a locking pawl is locked or unlocked, depending on whether there is positive or negative pressure in the chamber. This system is susceptible to leaks. Frequent opening and closing of the doors, and thus bending of the vacuum hoses, can eventually lead to breakage. The sealing rubbers in the air chambers of the locks can also deteriorate due to aging. In the event of a leak, one can check the vacuum with a vacuum pump by closing one line at a time, or inspect the system with a smoke machine to trace visible smoke.
The image below illustrates how many vacuum hoses were present in a Mercedes to pneumatically control the lock operation of the front doors and tailgate.
Electromagnetic:
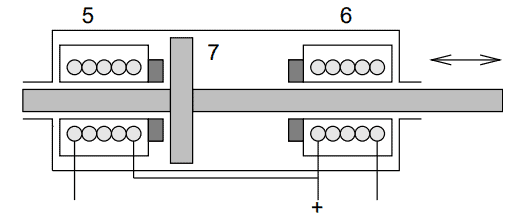
Electromagnetic central locking systems are equipped with dual magnets in door locks. One magnet provides the upward and the other the downward movement to lock or unlock the lock.
By energizing the correct electromagnet (5 or 6), the locking pawl is pressed into the correct position: locked or unlocked. Number 7 indicates the magnetic core.a0
This type of central locking system, like the pneumatic variant, is no longer used. The author could not find any wiring diagrams of a vehicle using this system.
Electric Motors:
Modern vehicles’ central locking systems are equipped with electric motors. The rotary motion of the motor is converted into a linear movement by a gear mechanism and a plastic mechanism. Usually, these electric motors do not have an end stop, and the mechanism locks up against the stop, blocking the electric motor.
To lock or unlock the electric motor, the current direction, and thus the movement direction of the electric motor, is reversed. The following wiring diagram shows the components in the central locking system of a modern car.
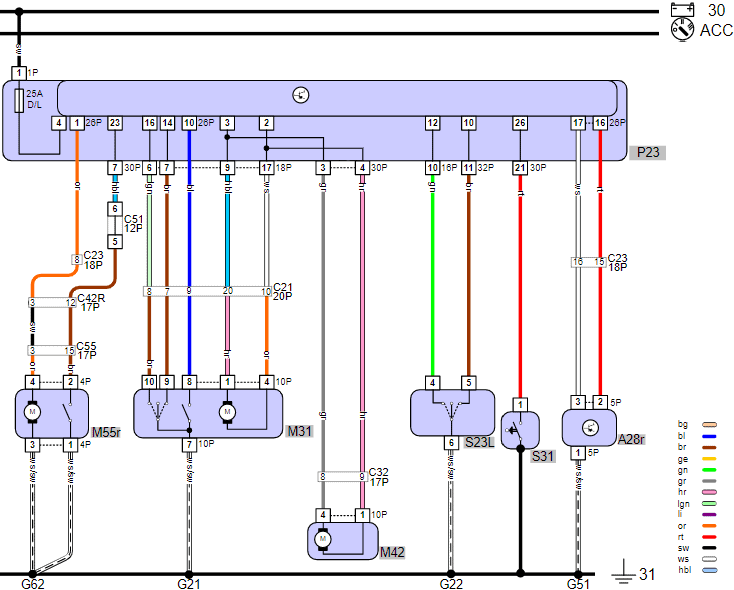
Legend:
- 30: battery positive
- 31: ground
- ACC: switched positive (terminal 15)
- P23: on-board network control unit
- M55r: tailgate lock unit
- M31: driver’s door lock unit
- M42: left rear door lock unit
- S23L: central locking switch
- S31: door contact switch left front
- A28r: central locking receiver
This diagram shows the driver’s door lock unit (M31) and the left rear door lock unit (M42). In reality, there are two more of these lock units (right front and right rear) in the diagram, but they have been removed due to size. We also see the tailgate lock unit (M55r) and the central locking switch (S23L) which is integrated into the dashboard, center console, or door trim. The switch S31 is separately integrated into the B-pillar, but in some cars, this switch is integrated into the lock unit. Finally, we see A28r: the radio receiver for the central locking where the signal from the remote control is received. The control unit P23 processes the signals from the switches to control the locks and, if necessary, the lights and indicator lights.
The following two images show a Volkswagen Golf mk5 door lock, one unlocked and one locked. In the locked state, this type of lock can also be double locked, the so-called “safe lock”. The next paragraph explains this double locking.
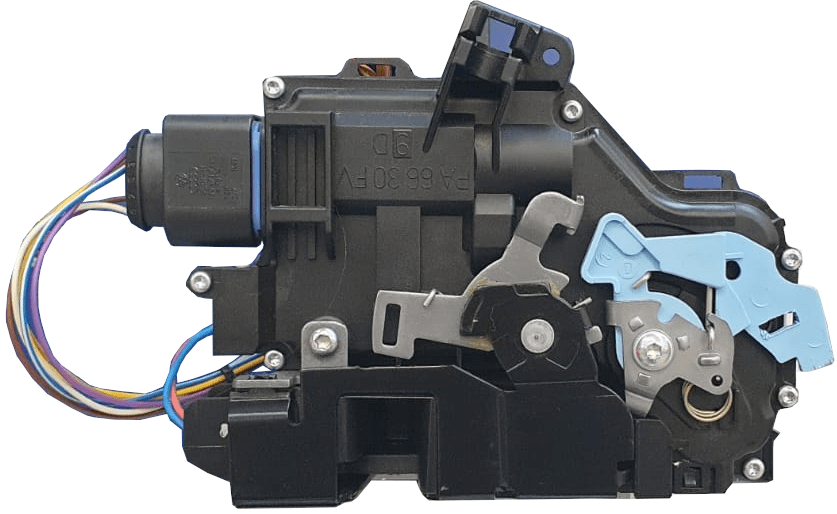
When the remote control is used to lock, the double locking is activated. In the image above, the mechanism with the light blue plastic part rotates counterclockwise to the left. The lock cannot be unlocked unless the double locking is activated.
Double locking prevents the lock from being unlocked when the inner handle is operated. This way, someone who breaks a window cannot open the door from inside. Activating the double locking can vary from car to car:
- Pressing the lock button on the remote once locks the lock “normally”. Only when pressing the lock button twice is the lock double locked;
- Upon the first lock button press, the lock is already double locked.
The following diagram shows the door module (below) of a VW Golf mk5, with above it the control unit (A32m) responsible for operating the lock.
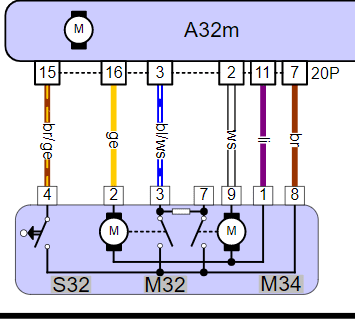
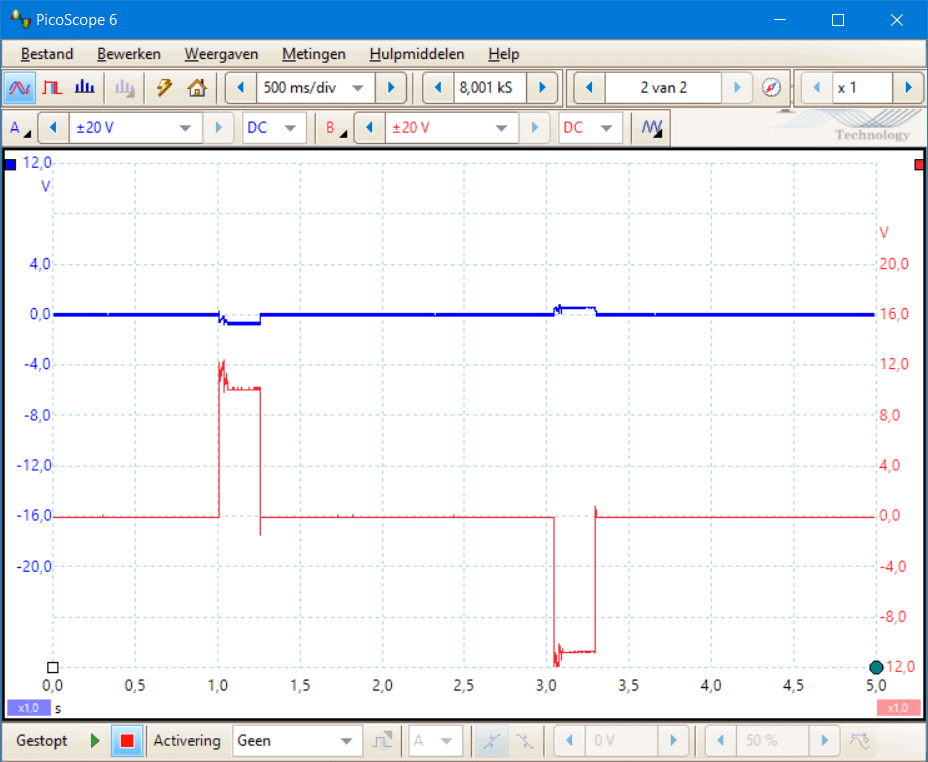
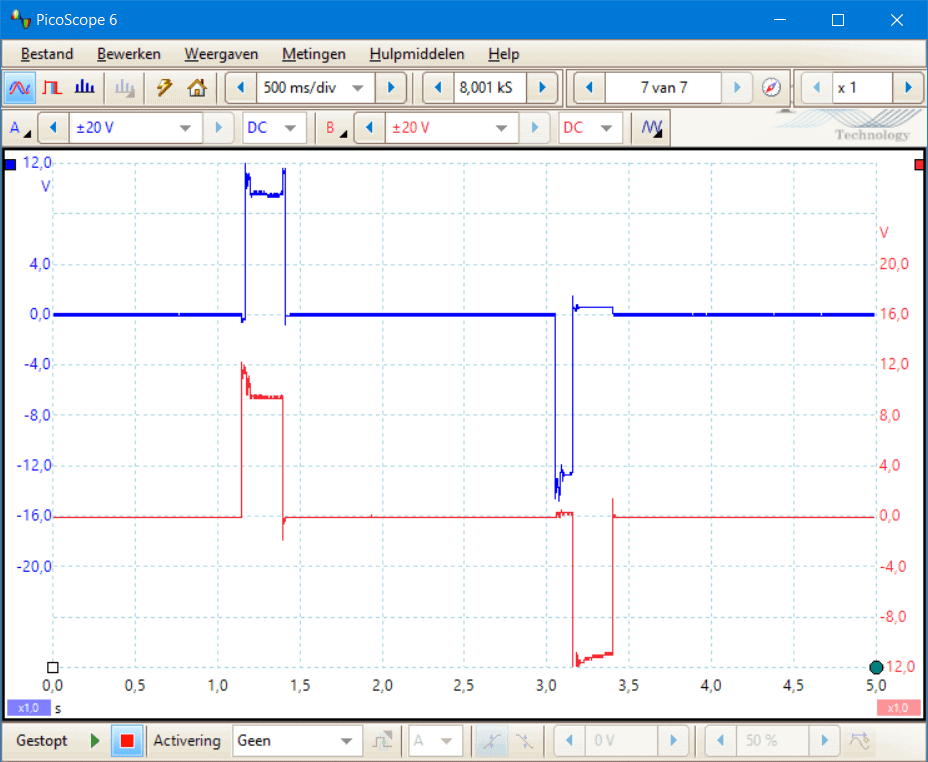
The following two oscilloscope images were recorded during the locking and unlocking of the door lock of this VW Golf.
- Channel A (blue) is connected to pin 9, the white wire on M34: this is the double locking motor;
- Channel B (red) is connected to pin 2, the yellow wire on M32: this is the locking motor.
The first oscilloscope image was recorded when locking with the interior switch and the second with the remote control. At the time t = 1.0 s in both oscilloscope images, the lock is locked, and at t = 3 unlocked. In reality, the time is multiplied by the number of ms/div; in this case, 500. When locking with the interior switch, we see that the locking motor (red signal) locks the lock, but that the double locking motor (blue signal) is not activated. We do see this in the second oscilloscope image; here, the double locking motor is activated. Here, the lock is locked and unlocked with the remote control. With double locking, the doors cannot be opened from inside.
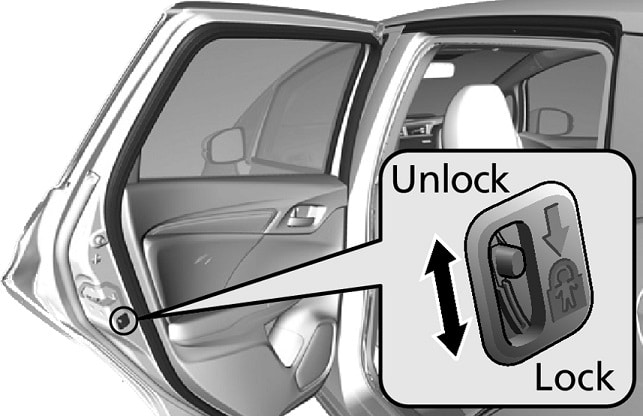
Child Lock:
The rear doors contain a switch with which the child lock can be activated. When the child lock is activated, rear passengers cannot open the door from the inside. When you operate the handle, there is no noticeable resistance, and nothing happens. Children cannot open the door themselves. The child lock operates independently of the door locks; it does not matter if the locks are locked using the central locking system.
The type of switch depends on the manufacturer: sometimes, it’s a lever to be moved with fingers, and other times, the key must be inserted into a slot to turn the switch.