Introduction:
Engines, of course, need to be cooled. The gasoline in a gasoline engine also contributes to cooling. With higher engine loads, the mixture is enriched. This results in an excess of fuel, which, among other things, ensures that the combustion chamber (the cylinder) is cooled from the inside. This occurs because the gasoline absorbs extra heat during evaporation. This helps prevent detonation, where the fuel ignites uncontrollably due to the high temperature of the engine components.
Injecting water into the cylinder also cools the components in the combustion chamber. If an engine is equipped with water injection, no additional fuel needs to be injected to provide cooling; this results in lower fuel consumption and more engine power.
Water in water injection is not used as fuel, as is the case with hydrogen. These techniques should not be confused!
Operation of Water Injection:
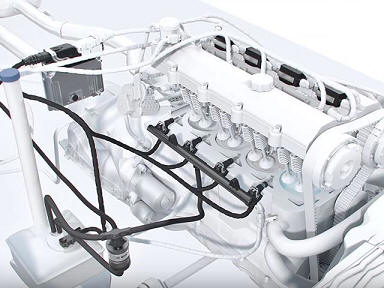
The water injector can be mounted in the cylinder head or in the intake manifold of a gasoline engine. This can occur with the injection of gasoline fuel as well as the liquid or gaseous injection of hydrogen used as fuel. The water injector should be as close as possible to the intake valve.
When extra cooling in the combustion chamber is desired, the water injector is controlled by the ECU. This will happen when power is demanded (such as during acceleration or driving at high speeds) and there is a risk of knocking. Therefore, water injection is also called “anti-detonation injection.” In cars where only RON98 can be used, water injection can also be a solution to tank RON95, as the water vapor prevents detonation phenomena.
An external water pump provides the water pressure in the injector line. When the injector is controlled by the ECU, it will open and a water mist will be injected. The water mist mixes with the incoming air in the combustion chamber before the intake valve. The small water droplets evaporate immediately and absorb a portion of the heat present in the combustion chamber.
The resulting water vapor exits through the exhaust. Because the amount of injected water is minimal, there are no risks of rust or oxidation of the engine components. The water reservoir must be periodically filled with distilled water.
In the image below, the water injector is placed in the cylinder head.

Engine power also increases with the use of water injection. Higher turbocharger boost pressure and earlier ignition are possible without the risk of detonation.
For example, the power of the BMW M4 GTS increases by no less than 37kW with water injection. This is a power gain of approximately 10% compared to the “standard M4.” This is accompanied by a fuel saving of up to 13% in situations where a rich mixture is desired; during acceleration and driving at high speeds.
The engine can also run effortlessly without water injection. However, maximum performance cannot be achieved because there is a lack of cooling. Without the use of water injection, there will be a limitation on engine power.

