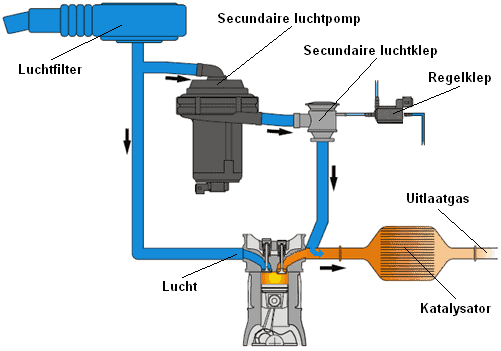
Function of the secondary air pump:
A gasoline engine always has a rich mixture during a cold start. This means that there is an excess of fuel, thus less oxygen. Because the catalytic converter is not yet at operating temperature during a cold start, it will not yet clean the exhaust gases. This means that the cold start results in the emission of a large amount of carbon monoxide (CO) and unburned hydrocarbons (HC). The purpose of the secondary air pump is to warm up the catalytic converter more quickly.
With a secondary air pump, outside air is added to the exhaust path. The extra air is directed into the exhaust before the catalytic converter. The addition of the extra air leads to an exothermic reaction. Exothermic means that heat is generated because the present CO and HC components burn when they come into contact with the additionally supplied air. This raises the temperature of the exhaust gas. Due to the higher exhaust gas temperature, the catalytic converter will also warm up quickly, so that during a cold start, the harmful components in the exhaust gases are reduced as quickly as possible .

Operation of the secondary air pump:
The secondary air system is located between the air filter and the exhaust. On the intake pipe from the air filter, there is a branch to the secondary air pump. From the secondary air pump, an air hose runs to the secondary air valve. This air valve is only open when the engine is cold and the air pump is working. When the air pump is turned off, the air valve is closed, otherwise the exhaust gases could flow back to the air pump. The opening and closing of the air valve is regulated pneumatically (with vacuum) by the control valve, which is operated by the engine’s ECU.
The outside air is directly supplied to the exhaust gas. In the exhaust, the exhaust gas will heat up immediately. As a result, the catalytic converter reaches its operating temperature (from 250° Celsius) in a short time. When the air pump is operational, it can be audible. The sound is often reminiscent of a vacuum cleaner. The pump usually switches off again between 20 and 30 seconds after the cold start because the catalytic converter is then sufficiently warmed up.
The additionally supplied air is recognized by the lambda sensors. In the event of a defect in the secondary air system, such as a sticking air valve or leakage in the hoses, the lambda sensors will detect the deviation. The engine management will illuminate the emission light on the dashboard. After all, with a defect in the secondary air system, more harmful substances are emitted. A defect in the secondary air system does not affect the operation of the engine.
�a
In addition to the secondary air system, the exhaust gas recirculation system (EGR) also provides post-treatment of the exhaust gas.
