Introduction:
GPS stands for Global Positioning System. GPS consists of a network of satellites orbiting the earth. These satellites constantly broadcast their locations. GPS receivers in navigation devices need 3 to 8 satellites to accurately determine the position and (driving) direction on earth to within a meter. a0
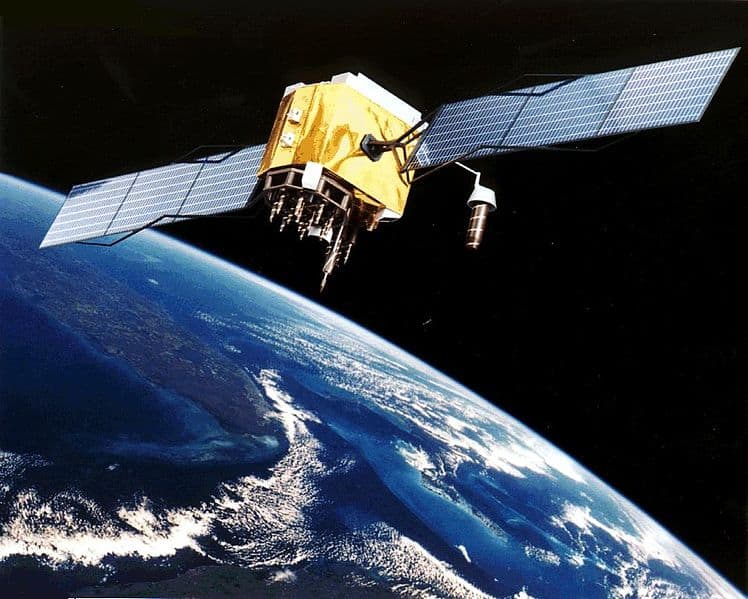

Positioning:
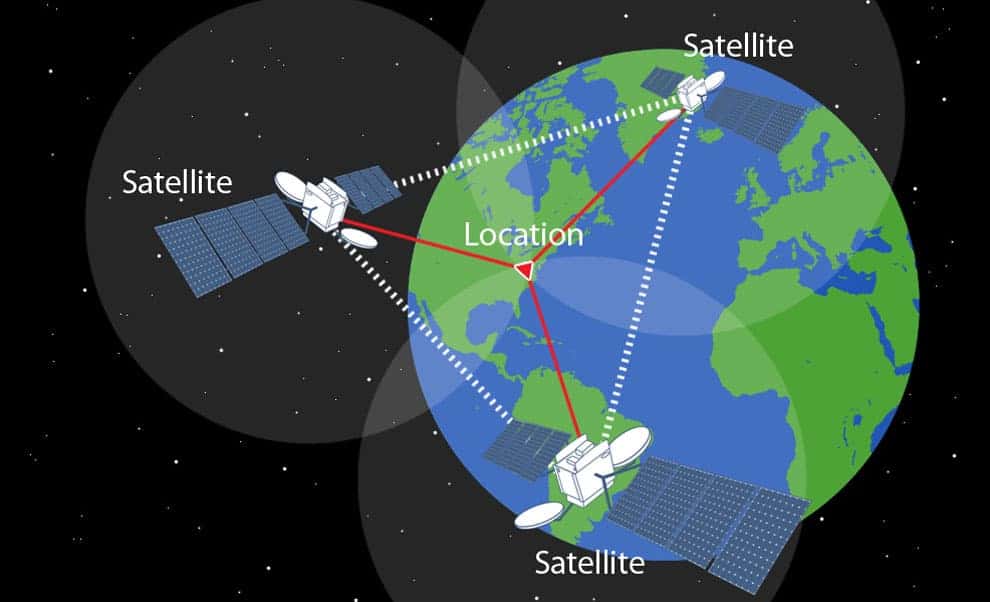
For positioning, 24 satellites are used that orbit the earth at an altitude of approximately 20,000 km. The positions of the satellites are determined such that at least five satellites cover the same point on earth simultaneously.
With a minimum of three satellites, a three-dimensional space can be calculated if we know the distance between three fixed points. Positioning is conducted by calculating the time between sending and receiving signals. We can calculate the distance between the receiver and each satellite by multiplying the time by the speed of light (300,000 km per second). When we do this with at least three satellites, we can draw imaginary lines to a common point. A fourth satellite increases the accuracy of the positioning.
The position is displayed by the receiver in longitude and latitude degrees. a0The equator is at 0 b0 and the poles at 90 b0. The lines of longitude (meridians) connect the poles. Meridians are imaginary lines over the earth:
- perpendicular to the equator;
- from pole to pole.
