Subjects:
- Preface
- Standard fuse
- Mini fuse
- maxi fuse
- Cartridge fuse
Preface:
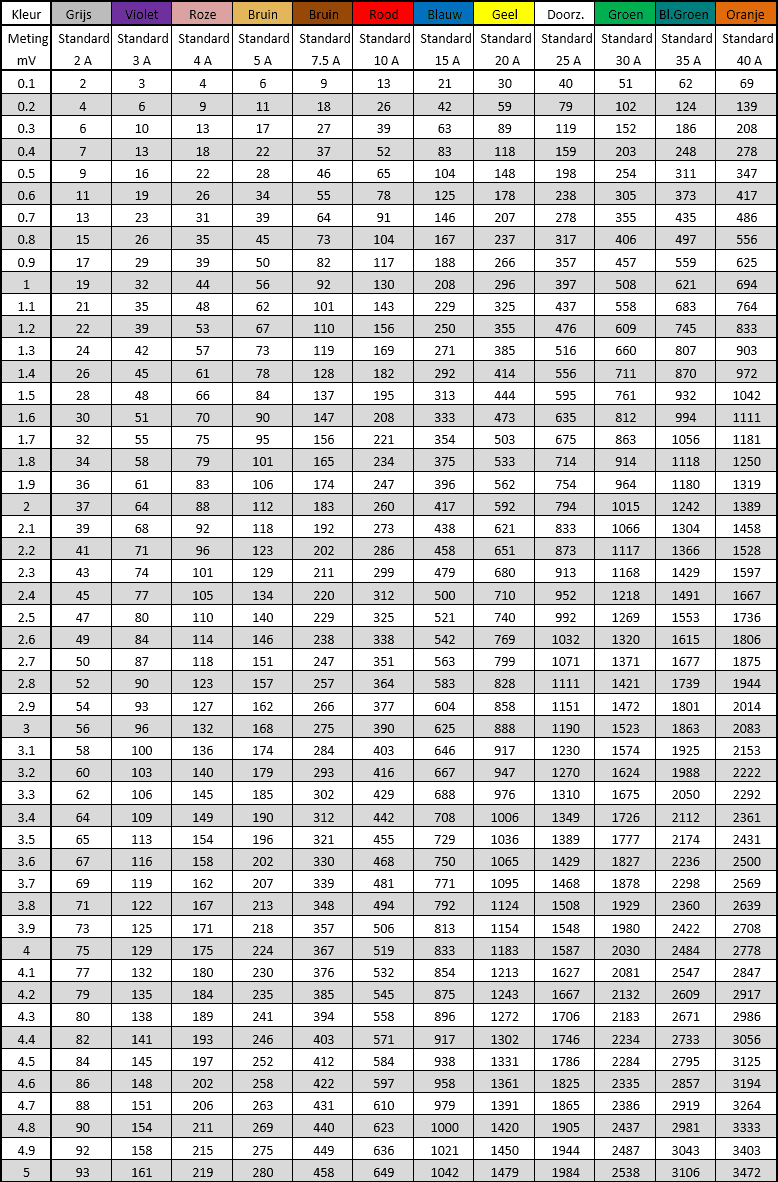
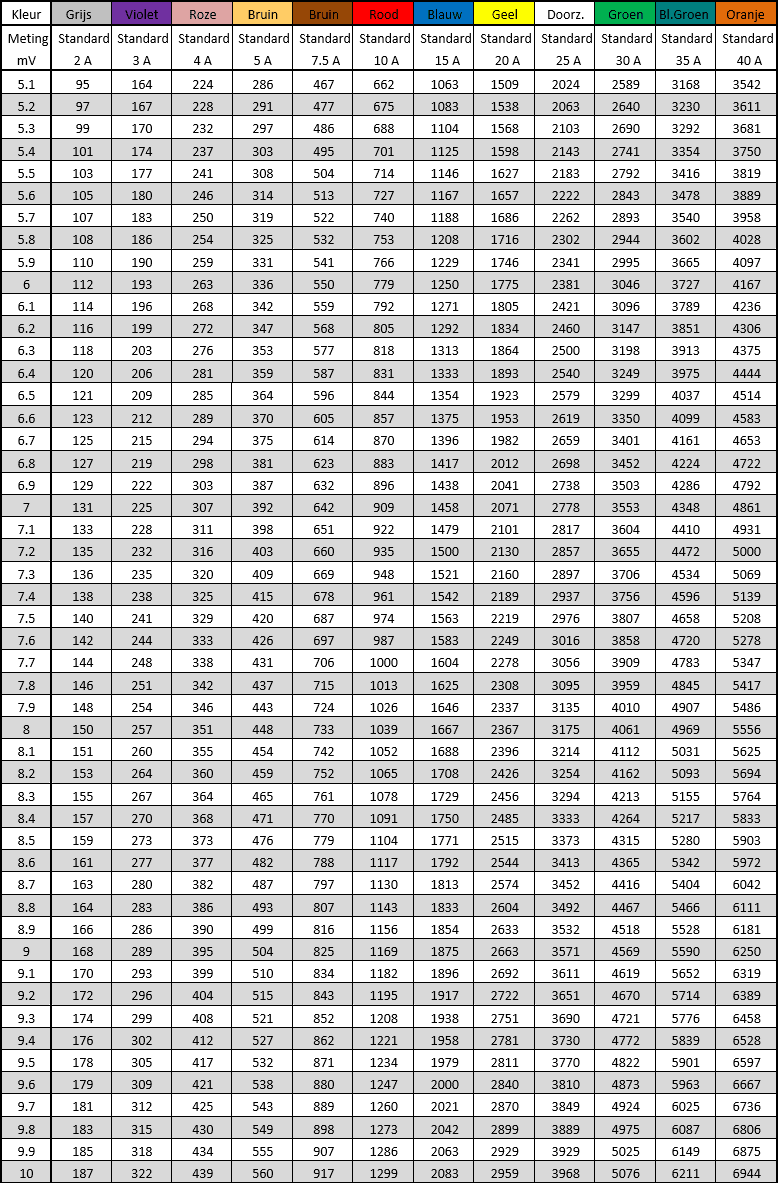
When diagnosing, it may be helpful to check the voltage drop across fuses to check. The current through the fuse influences the voltage difference on the contact surfaces of the fuse. For example, in the connected state, by measuring the voltage drop, we can determine whether current flows through the fuse. Depending on the type of fuse and its nominal value, we can look up the current in tables. These tables are shown on this page.
Standard fuse:
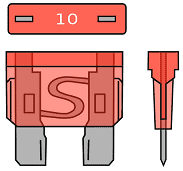
In passenger cars we usually find plug-in fuses in the “mini” and “normal”, ie the standard dimensions. The standard blade fuse is coded “ATO”. An example of this can be seen in the following image. Here are the side, top and front views of a red 10 Amp fuse.
The tables below show the voltage drop across the fuse. The voltage drop indicates how much voltage is absorbed into the fuse. The voltage drop depends on the current through the fuse and the fuse.
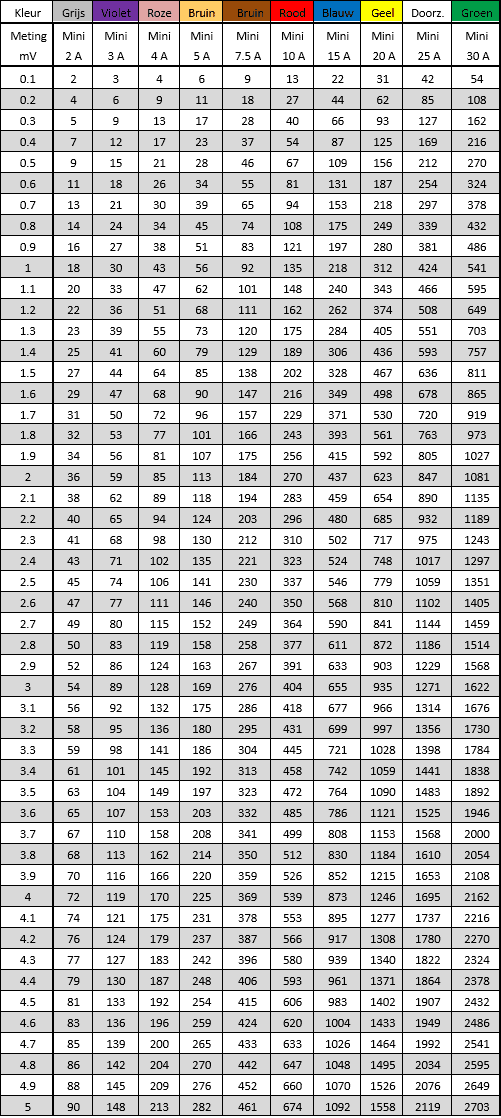
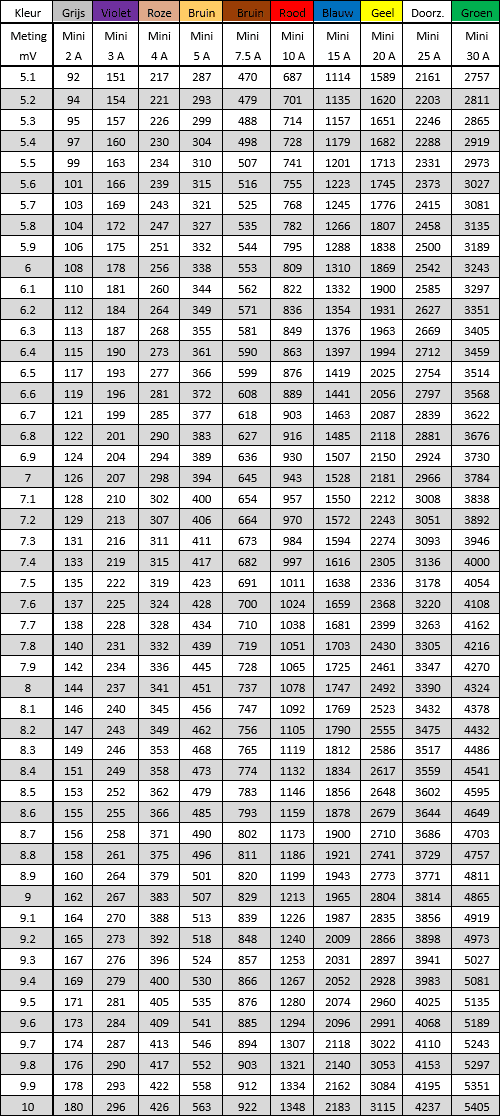
Mini fuse:
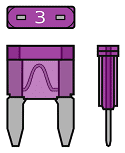
In addition to normal ones, we also find mini plug-in fuses in the fuse boxes of passenger cars. The mini fuse is, as the name suggests, a smaller variant of the normal fuse. An example of this can be seen in the following image: this concerns a violet fuse with a 3 Ampere fuse.
The two tables below show the voltage drop across the various fuses with increasing current.
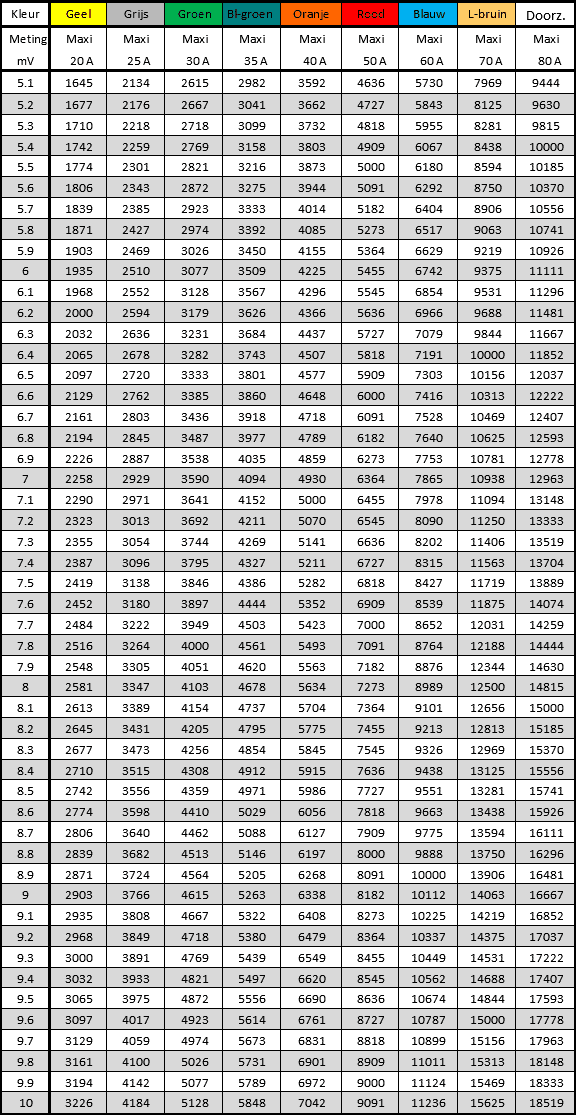
Max fuse:
The maxi fuse is the largest type of blade fuse we find in passenger cars. This type of fuse is suitable for high powers.
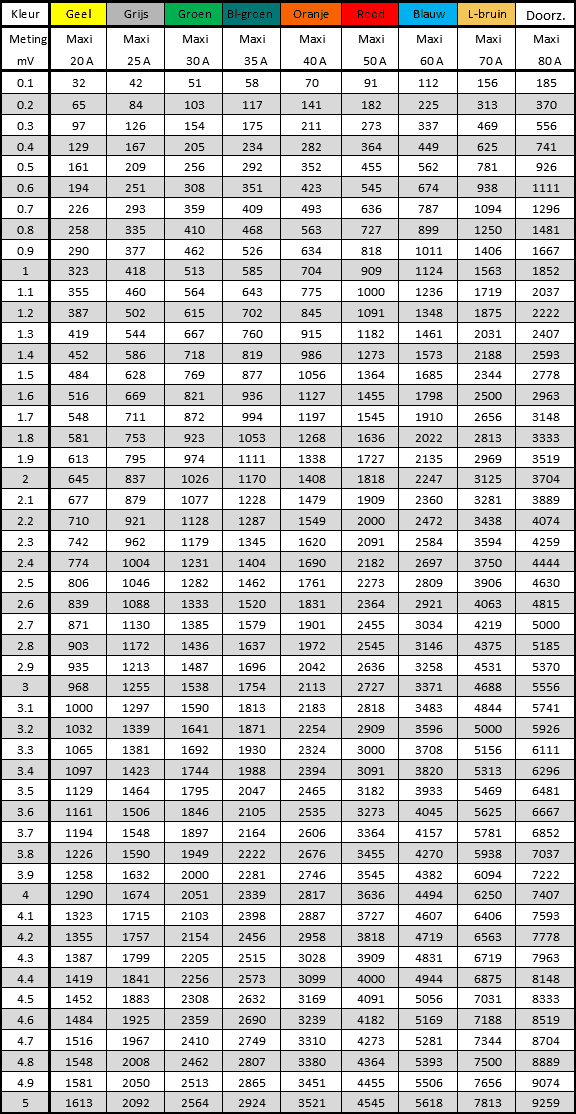
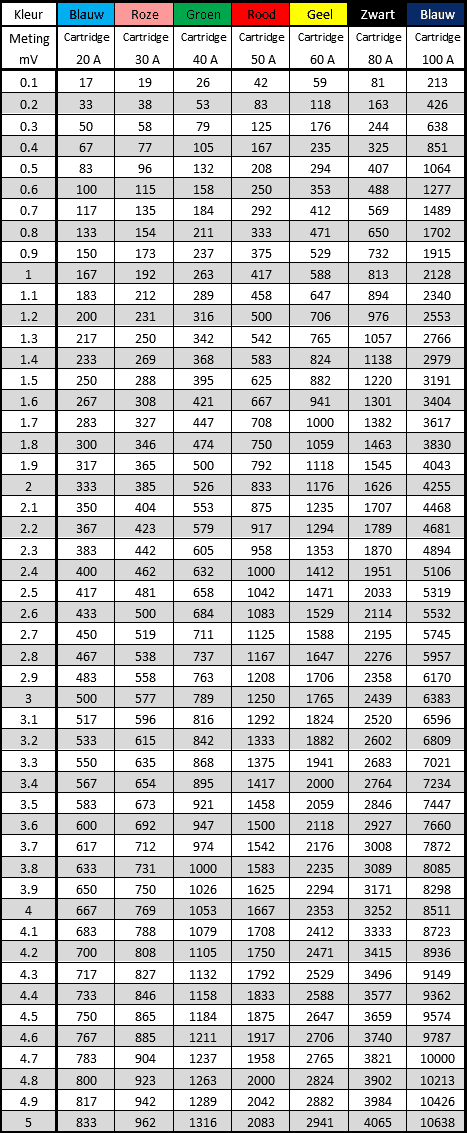
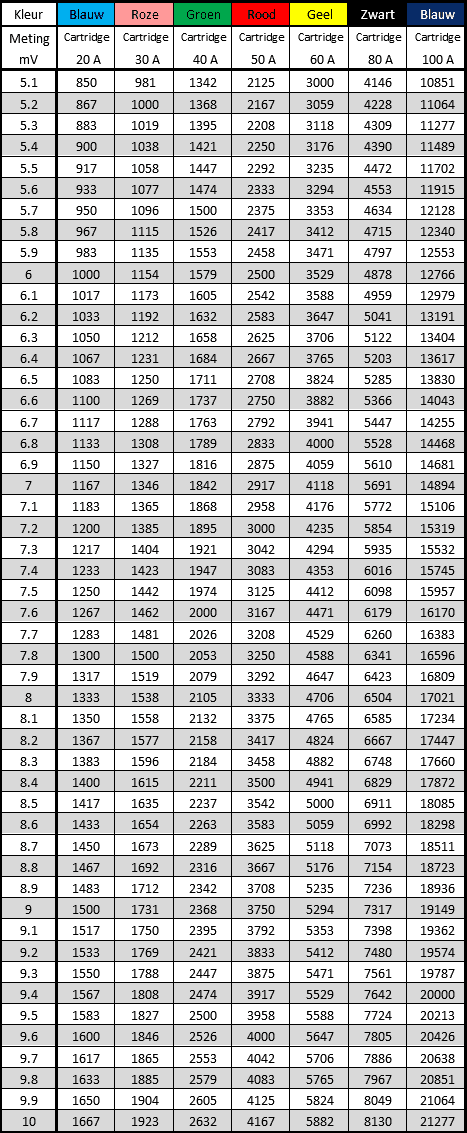
Cartridge fuse:
This type of fuse is often found in Japanese and Korean cars. The cartridge fuse consists of a square plastic housing with a transparent cover. The housing can be long or short. You can see the fuse wire in the transparent cover and recognize whether the fuse is still intact.
The tables below show the voltage drop across this fuse type.

Related pages:
