Subjects:
- TPMS general
- Passive TPMS
- Active TPMS
- Learning TPMS sensors
TPMS general:
TPMS (Tyre Pressure Monitoring System) is a safety system developed in the 90s for vehicles fitted with run-flat tyres. The TPMS warns the driver of the vehicle when the tire pressure of a tire becomes too low. The system starts working from 0,5 bar. If there is a puncture, the driver will be informed about this in good time, before a dangerous situation arises.
There are different versions of the TPMS:
- Passive: This uses the ABS sensors in the vehicle.
- Active: uses pressure sensors in the tires.

Passive TPMS:
By measuring the speed at which the wheels rotate, a pressure loss in a tire can be recognized. The speed of the wheels is measured by the ABS sensors. The tire pressure is therefore not measured. When a tire becomes too soft, the rolling circumference of the tire in question will decrease. The wheel will rotate at a slightly higher speed. The increase in speed is recognized by the computer as a pressure loss.
The figure below measures the FM (Frequency Modulation) signal from an ABS sensor. This signal is formed on the basis of the speed of the wheel. If one of the four sensors of the wheels transmits a different signal, the computer will detect a tire pressure that is too low.
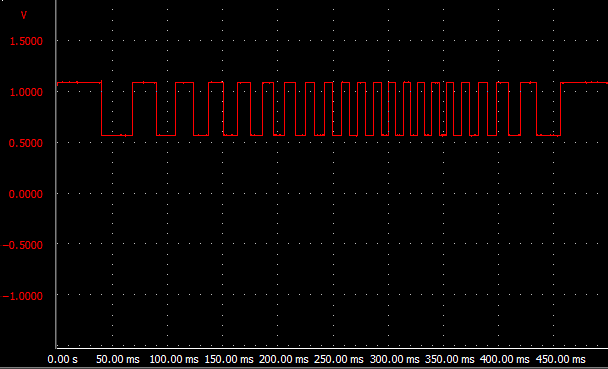
While driving, there are several conditions that the system takes into account; Bouncing in and out or driving around bends do not affect the system's operation. An indicator light will not immediately light up after a difference in wheel speeds has been discovered. The control is carried out over a longer distance. If the deviation occurs this specified distance, the system will illuminate the warning light.
Changing the tire pressure obviously also affects the system. After the tires are inflated, there will be small speed differences between the four wheels. Therefore, the system must be reset or initialized after changing the tire pressure. The initialization can be carried out by locating it in the menu of the on-board computer, or by pressing the button on the dashboard with the tire icon (see picture).

Often the button has to be pressed for a few seconds, so that the TPMS is reset. Often an icon will appear in the dashboard and will disappear after a few seconds. This is a sign that the system is ready for use again. The system will automatically adjust itself while driving; the wheel speeds are stored while driving a long distance. The system is therefore reliable again after driving a few kilometers.
If the system is reset while the Check Engine Light is on, the system will reset itself based on the current wheel speeds. The flat tire is therefore no longer recognized.
Active TPMS:
The active TPMS uses pressure sensors in the tire. These TPMS sensors constantly send information about tire pressure and tire temperature to the computer via an FM frequency. The system can already detect a flat tire when the car is stationary. Some systems even monitor the tire pressure of the spare wheel.
Since the active TPMS monitors tire pressure, this will also make a positive contribution to fuel consumption, tire wear and road safety; the driver cannot forget to check the tire pressure in time.
This is possible because there are pressure sensors in the tires, which continuously transmit the tire pressure to the control unit. The control unit checks that the pressure remains the same. Only when the tire pressure has dropped will a warning light appear in the instrument panel. Nowadays, tire pressure is often shown graphically on the on-board computer display. This is only possible when the TPMS is equipped with EZ sensors. This is explained in another section on this page.
The image shows a mounting overview of an EZ sensor. This is a widely used TPMS sensor that can be mounted in any rim. The standard valve is replaced by this sensor. Built into the sensor is a battery that lasts about 10 years.
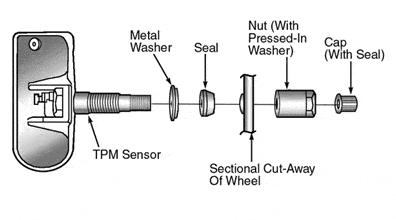
The EZ-sensor can be easily installed in the rim by mounting the two parts (the sensor part and the valve part) together with screws.
The TPMS sensors transmit tire pressure and temperature to the control unit. Modern, advanced systems make this clear to the driver by displaying it graphically. In this way the driver can keep an eye on the tire pressure.
The display will show the location of the flat tire with the measured pressure. The driver can then make a decision to continue to the garage, or to stop immediately because the tire is empty. Under no circumstances should the tire pressure be less than 1.0 bar.


Replacing tires does require extra attention. Pressing the bead into the low bed of the rim may cause the tire to move against the TPMS sensor. This can cause the sensor to break. Therefore, the location of the valve must always be taken into account. At that point, it must be prevented at all times that the tire presses against it.

Learning TPMS sensors:
When the wheels are switched from left to right, or from front to back, the position of the TPMS sensor changes. The computer must know in which positions the sensors are mounted. If the sensors are not taught in properly, the tire pressure indicator light on the left front wheel would illuminate, while the right rear tire is flat. After replacing tires or changing the positions of the wheels, the sensors must be taught-in. The way in which the sensors must be taught-in differs per manufacturer.
All sensors have a read-in code:
- A = automatic learning while driving.
- O = teach in via OBD using diagnostic equipment.
- S = explanation is in the user manual.
The location of the sensors that are automatically taught while driving is determined on the basis of a number of data. During acceleration, braking and steering, the wheels make different speeds relative to each other. During steering, the wheels on the inside turn will turn more slowly than the wheels on the outside, and during acceleration, the wheels on the driven axle will make a slightly higher speed than the non-driven wheels. The latter has to do with a maximum permitted wheel slip that is caused by the deformation of the tyre.
During the ride, the locations of the sensors are determined, whereby the front tang is often shown as a percentage.
There are also sensors that must be taught in with diagnostic equipment. There are several different types in this. With all types, a readout and programming computer must be kept close to the relevant TPMS sensor. In this computer, the correct position must be selected in advance. After the computer has made wireless contact with the sensor, the correct data is entered into the sensor. A test drive must then be taken to activate the TPMS system. The computer is shown in the picture.
There are also variants in which a readout and programming computer is linked to the readout computer, which in turn is connected to the car via the OBD plug. The values are stored in the TPMS sensors as well as in the vehicle's control unit. In most cases, no test drive is required; the control system is immediately active.

