Subjects:
- NOx sensor general
- NOx sensor operation
NOx sensor general:
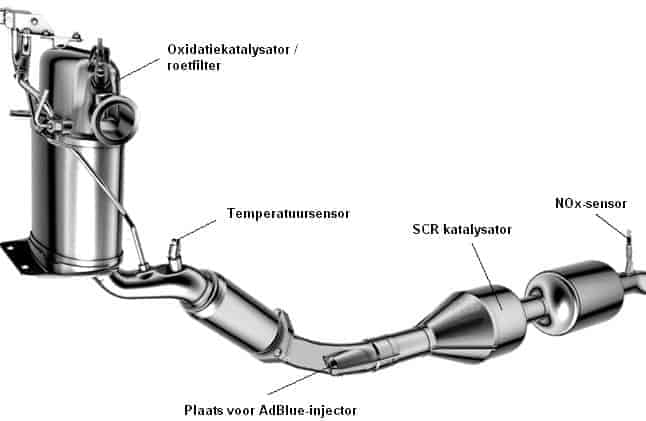
The NOx sensor is located immediately after the Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR Catalyst) mounted in the exhaust. The NOx sensor checks whether NOx is still present in the exhaust gases. If that is the case, the harmful substances in NOx have not been sufficiently converted into the harmless substances nitrogen (N2) and water (H2O). In that case there will be more AdBlue are injected.
The NOx sensor is used not only in systems with an SCR catalytic converter and Adblue, but also in systems with only a NOx storage catalyst applied. In the latter system, the storage catalyst will be regenerated by temporarily applying a richer mixture; additional fuel is then injected.

NOx sensor operation:
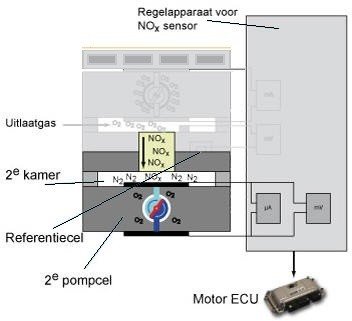
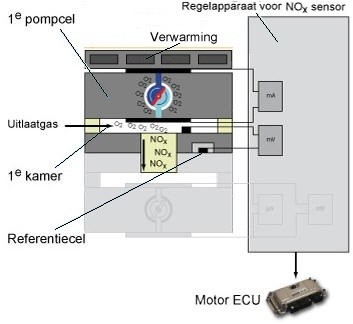
The illustration shows the components of the NOx sensor and control unit. The NOx sensor consists of two chambers, two pump cells and a heating element. The sensor element consists of zirconium dioxide; this substance has the property that when an electronic voltage is applied, the negative oxygen ions flow from the negative electrode to the positive electrode.
Part of the exhaust gas is collected in the first chamber. There the oxygen concentration is reduced, so that the nitrogen oxide content in the exhaust gas can be measured. An electrical voltage can be measured at the electrodes on the basis of different oxygen contents in the exhaust gas and the reference cell. The NOx sensor control unit regulates this voltage to a constant value. The value corresponds to an air/fuel ratio of lambda = 1. To achieve this, oxygen is pumped into or out of the first chamber by the pump cell, and the oxygen concentration in the first chamber can be controlled to a certain value.
The exhaust gas flows from the first to the second chamber (see picture). The NOx molecules in the exhaust gas are split into N2 and O2 at a special electrode. Since the voltage at both the inner and outer electrodes is a constant 450mV, the oxygen ions move from the inner to the outer electrode. The current flow through the oxygen pump is indicative of the nitrogen content in the second chamber. Since the flow through the oxygen pump is equal to the nitrogen oxide content in the exhaust gas, the amount of nitrogen oxides can be determined on this basis.
The NOx sensor cannot operate until the temperature of the exhaust gases is high enough. At that moment there will no longer be any condensed water present and the measurement will not be affected by this. The measured signal is sent from the NOx sensor control unit to the engine control unit.