Subjects:
- MOST bus
- Communication protocols
- MOST25
- MOST50
- MOST150
- Locate fault
MOST bus:
Today, the MOST bus is increasingly used in audio systems. MOST stands for: Media Oriented Systems Transport. The MOST bus is a ring-shaped network that uses light conduction. Each control unit in the network transmits optical signals with its own LED via a fiber optic cable. The frequency with which the LED flashes forms a signal that eventually leads to a message that can be received by other control units. The image below shows a plug with a light signal.
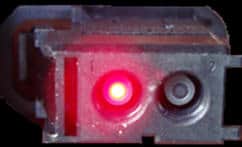
The MOST bus is extremely fast due to a combination of LEDs and fiber optic cables. Both audio and video material can be sent and received via the MOST. Below is a MOST bus network used in a car's audio system. This includes the radio, display, amplifier, entertainment computer, DVD changer and instrument panel.
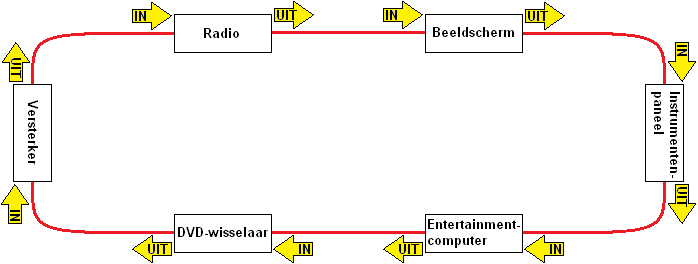
For example, a telephone can be connected via the entertainment computer where music is streamed via bluetooth. Music or movies can also be played via the DVD changer. The data is passed on to the other control units in the network by means of the fiber optic cable. The images will appear on the screen, the audio will be played by the amplifier over the speakers.
The data arrives at the control unit, after which it is forwarded to the next control unit. When one control unit is disconnected, the light beam will be interrupted and no more data transfer will be possible.

The image on the right shows a fiber optic cable. Because the cable allows light to pass through, it is important that the cable is not kinked. If this is done, for example because the cable has become jammed behind the glove compartment, the light beam can be interrupted or weakened. Components in the MOST circuit will no longer be able to be controlled properly. The technician's job is to locate the cause of the failure. This can take a lot of diagnosis time.

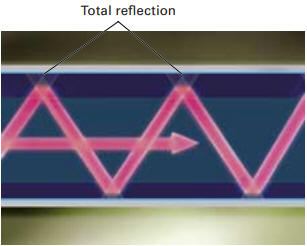
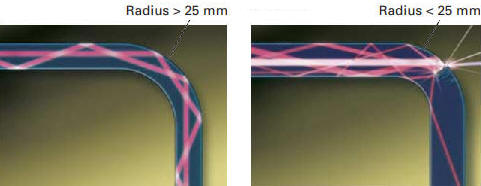
The light signals are reflected in the cable. If a bend is too sharp, the signal in the cable can no longer be reflected cleanly. This can be seen in the images below. When mounting this optical cable, it is therefore necessary to take into account the laying of the cable with large loops where it has to make a bend. The radius of the bend must be more than 25 mm.
Communication protocols:
There are several generations of the MOST bus. The first generation was the MOST25, with a data rate of 25 Mbit/s. MOST50 (50 Mbit/s) was the successor of MOST25. The latest variant is the MOST150 (150 Mbit/s), whereby the data rate is 6x higher than the first generation. Not only the data rate differs per generation, but also the content and structure of the data frames. The differences herein are described in the following paragraphs.
MOST25:
With the MOST25, the data rate is 25 Mbit/s (megabits per second). This means that 25 x 1.000.000 bits, so 25.000.000 bits per second are sent. Another feature of the MOST25 is that messages are sent in data blocks, each consisting of 16 frames. Each frame consists of 512 Bits (0 to 511). That is equal to 64 bytes. The image below shows an example of a data block.
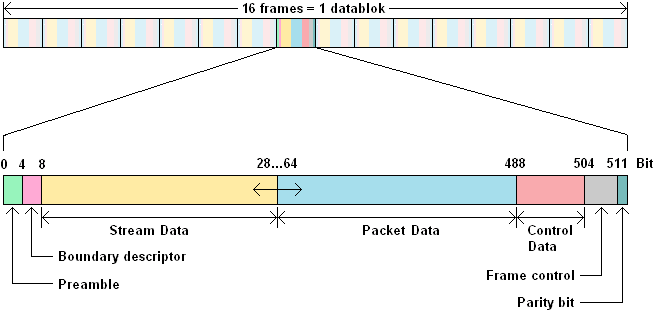
- Preamble: The preamble (meaning opening or introduction) synchronizes the tranceivers prior to the message.
- Boundary descriptor: Indicates how many of the available 60 bytes are divided into the synchronous and asynchronous bytes.
- Stream data: continuous data transfer (also called synchronous data) which requires a high bandwidth. Used for the continuous data transfer of video and audio.
- Packet data: data transfer by means of packets (therefore also called asynchronous data) in which large data blocks are sent. These data blocks mainly consist of information for calculation purposes and messages in the form of asynchronous data, such as GPS information. Also the packet data requires a high bandwidth.
- Control data: This data maintains the communication between the different network ports.
- Frame control: Controls the respective data frame.
- : Parity bit: Used to detect bit errors.
MOST50:
The MOST50 generation uses a data rate of 50 Mbit/sec. This is a doubling of the data rate of the MOST25. Not only is the data rate different from the MOST25, but also the length and structure of the frames are different. A MOST50 frame consists of 128 Bytes, which is equal to 1024 Bits. This is also a doubling compared to MOST25.
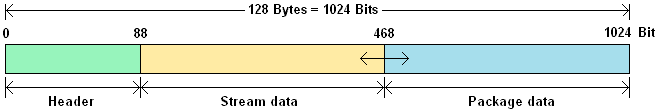
The layout of a data frame is also a lot simpler; a frame consists of:
- Header: Contains the administration, the boundary descriptor, 4 Bytes Control Data.
- Stream data: equal to MOST25.
- Package data: equal to MOST25.
MOST150:
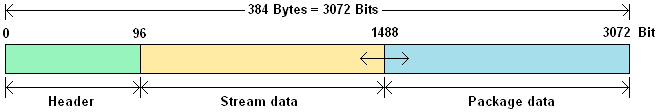
The MOST150 frames have a structure similar to that of MOST50 frames. The speed is 150 Mbit/sec, and contains 384 Bytes (3072 Bits), which is three times as high as the MOST50 frames.
Locating fault:
When the MOST bus is interrupted, the light signal can no longer be passed on to other control units. The result is that the screen remains black, no sound can be heard or other functions no longer work. This could have the following two causes:
- Fiber optic cable is interrupted.
- Control unit is defective.
An interrupted fiber optic cable can be caused by incorrect installation, causing it to get stuck (for example interior parts such as the glove compartment), but also because it is kinked. The kink causes a weakening of the light signal. The fiber optic cable should therefore be checked for damage, kinks or breakage. Because the fiber optic cable sometimes runs throughout the car, it can become an extensive search job. A damaged fiber optic cable is often the result of inexpert handling when installing a radio or dashboard parts. It is therefore advisable to start your search here.
The moment a light signal enters the control unit, but does not come out, it may be that the control unit is defective. It is possible that no faults are stored in the fault memory. The location of the defect can be checked by excluding this Control Unit from the MOST circuit. An example of this can be seen in the image below.
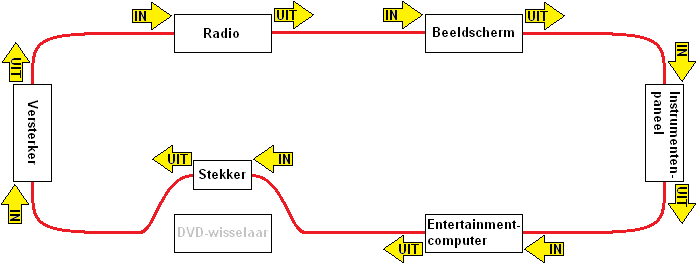
In this case, the DVD changer is no longer part of the MOST circle. The fiber optic cables that were connected to the control unit are now connected with a plug. The light signal is now transferred from one cable to the other. If communication does resume in this situation, the DVD changer may interrupt the light signal. This can of course also be tried with other control units, because the same type of plugs are connected to them.
Faults with diagnostic equipment can also be traced. This is usually referred to as a “ring fracture diagnosis”. More on this later…
The MOST bus is connected to the Gateway. The gateway allows communication with other types of networks, such as the CAN or LIN bus.
