Subjects:
- Calculate Piston Speed
Calculate piston speed:
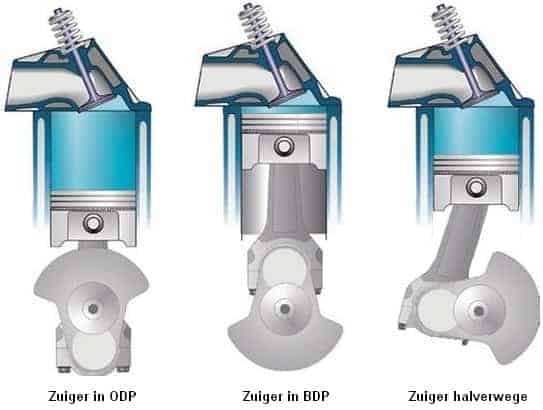
The speed at which the piston moves in the cylinder is called the piston speed. The piston moves from top to bottom (top dead center TDC) to bottom (bottom dead center ODP) and up again. Whenever the piston reaches TDC or ODP, it stops because the direction of movement changes. This is clarified in the image below:
Piston speed is highest when it is halfway up the cylinder. This is also related to the secondary piston movement. From the middle, the movement will slow down again until the TDC is reached. When the crankshaft turns one full turn, the piston moves down and up once. The distance between the TDC and the ODP is called the stroke volume. If the current crankshaft speed is also known, the average piston movement can be calculated.
V = 2 xsxn
V = average piston speed [meters per second]
2 = twice the piston movement
s = stroke; the distance the piston travels [meters]
n = crankshaft speed [Hertz]
Example:
A motor has a stroke of 90 mm. The displacement can be found in the factory data of the engine. The engine speed is 3000 revolutions per minute (read from the tachometer). With this data the average piston speed can be calculated.
To begin with, the stroke given in millimeters must be converted to meters (divide by 1000). So that's 0,09 meters. Also, the crankshaft speed in revolutions per minute must be converted to revolutions per second (divide by 60). That's 50 Hertz.
The calculated data can be entered in the formula:
V = 2 x 0,09 x 50 = 9 m/s
